Bezafibrate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Bezafibrate''' is a | {{Short description|A lipid-lowering medication}} | ||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002276 | |||
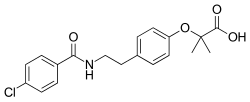
| IUPAC_name = 2-(4-(2-(4-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid | |||
| image = Bezafibrate.svg | |||
| image2 = Bezafibrate_synthesis.svg | |||
}} | |||
'''Bezafibrate''' is a [[fibrate]] medication used to treat [[hyperlipidemia]], a condition characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the blood. It is primarily used to lower [[cholesterol]] and [[triglyceride]] levels, thereby reducing the risk of [[cardiovascular disease]]. | |||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Bezafibrate | Bezafibrate works by activating [[peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors]] (PPARs), which are nuclear receptors that regulate the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism. By activating PPARs, bezafibrate increases the oxidation of fatty acids and enhances the clearance of triglycerides from the bloodstream. This leads to a reduction in [[very-low-density lipoprotein]] (VLDL) and [[low-density lipoprotein]] (LDL) levels, while increasing [[high-density lipoprotein]] (HDL) levels. | ||
== | ==Clinical Uses== | ||
Bezafibrate is indicated for the treatment of various forms of hyperlipidemia, including: | Bezafibrate is indicated for the treatment of various forms of hyperlipidemia, including: | ||
* | * [[Hypercholesterolemia]] | ||
* [[Hypertriglyceridemia]] | |||
* Mixed hyperlipidemia | |||
* | |||
* | |||
It is often prescribed when dietary | It is often prescribed when dietary measures and other non-pharmacological interventions have failed to adequately control lipid levels. | ||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Common side effects of bezafibrate include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Other potential side effects include: | |||
* [[Myopathy]] | |||
* [[Liver enzyme]] abnormalities | |||
* [[Gallstones]] | |||
Patients are advised to report any unexplained muscle pain or weakness, as this could indicate a serious condition known as [[rhabdomyolysis]]. | |||
==Contraindications== | ==Contraindications== | ||
Bezafibrate | Bezafibrate is contraindicated in patients with: | ||
* Severe renal impairment | * Severe [[liver disease]] | ||
* Severe [[renal impairment]] | |||
* Pre-existing gallbladder disease | * Pre-existing gallbladder disease | ||
==Drug Interactions== | ==Drug Interactions== | ||
Bezafibrate | Bezafibrate may interact with other medications, including: | ||
* [[Statins]]: Increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis | |||
* [[Anticoagulants]]: Enhanced anticoagulant effect | |||
== | ==Synthesis== | ||
[[File:Bezafibrate_synthesis.svg|thumb|right|Synthesis of bezafibrate]] | |||
The synthesis of bezafibrate involves the reaction of 4-chlorobenzoyl chloride with 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethylamine to form an amide intermediate. This intermediate is then reacted with 2-bromo-2-methylpropanoic acid to yield bezafibrate. | |||
[[ | ==Related Pages== | ||
[[ | * [[Fibrate]] | ||
[[ | * [[Hyperlipidemia]] | ||
* [[Cholesterol]] | |||
* [[Triglyceride]] | |||
[[Category:Lipid-lowering agents]] | |||
[[Category:Carboxylic acids]] | |||
[[Category:Chlorobenzenes]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:55, 23 March 2025
A lipid-lowering medication
| Bezafibrate | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Bezafibrate is a fibrate medication used to treat hyperlipidemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the blood. It is primarily used to lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Bezafibrate works by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are nuclear receptors that regulate the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism. By activating PPARs, bezafibrate increases the oxidation of fatty acids and enhances the clearance of triglycerides from the bloodstream. This leads to a reduction in very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels, while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Bezafibrate is indicated for the treatment of various forms of hyperlipidemia, including:
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Mixed hyperlipidemia
It is often prescribed when dietary measures and other non-pharmacological interventions have failed to adequately control lipid levels.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of bezafibrate include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Other potential side effects include:
- Myopathy
- Liver enzyme abnormalities
- Gallstones
Patients are advised to report any unexplained muscle pain or weakness, as this could indicate a serious condition known as rhabdomyolysis.
Contraindications[edit]
Bezafibrate is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe liver disease
- Severe renal impairment
- Pre-existing gallbladder disease
Drug Interactions[edit]
Bezafibrate may interact with other medications, including:
- Statins: Increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
- Anticoagulants: Enhanced anticoagulant effect
Synthesis[edit]

The synthesis of bezafibrate involves the reaction of 4-chlorobenzoyl chloride with 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethylamine to form an amide intermediate. This intermediate is then reacted with 2-bromo-2-methylpropanoic acid to yield bezafibrate.