Lower motor neuron lesion: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
==Causes== | | name = Lower motor neuron lesion | ||
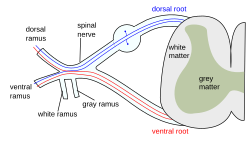
Lower motor neuron lesions can | | image = [[File:Spinal_nerve.svg|250px]] | ||
* [[Trauma]] to the | | caption = Diagram of a spinal nerve, which can be affected in lower motor neuron lesions | ||
* [[Infection]] | | field = [[Neurology]] | ||
| symptoms = [[Muscle weakness]], [[muscle atrophy]], [[fasciculations]], [[hypotonia]], [[areflexia]] | |||
| complications = [[Paralysis]], [[muscle wasting]] | |||
| onset = Varies depending on cause | |||
* [[ | | duration = Can be chronic or acute | ||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[infection]], [[autoimmune disease]], [[genetic disorders]] | |||
| risks = [[Injury]], [[viral infections]], [[genetic predisposition]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[electromyography]], [[nerve conduction studies]] | |||
* [[ | | differential = [[Upper motor neuron lesion]], [[myopathy]], [[neuropathy]] | ||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[occupational therapy]], [[medications]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; depends on underlying cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in certain conditions like [[spinal muscular atrophy]] | |||
}} | |||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Lower Motor Neuron Lesion}} | |||
==Diagnosis== | A '''lower motor neuron lesion''' refers to damage or dysfunction of the [[lower motor neurons]] (LMNs), which are responsible for transmitting signals from the [[upper motor neurons]] to the [[skeletal muscles]]. These neurons are located in the [[anterior horn]] of the [[spinal cord]] and the [[cranial nerve nuclei]] of the [[brainstem]]. Lower motor neuron lesions can result in a variety of clinical manifestations, including muscle weakness, atrophy, and diminished reflexes. | ||
== Anatomy of Lower Motor Neurons == | |||
* [[ | Lower motor neurons originate in the [[central nervous system]] but extend their axons into the [[peripheral nervous system]]. They are the final common pathway for motor commands that initiate voluntary movement. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the [[ventral horn]] of the spinal cord and in the motor nuclei of cranial nerves. | ||
=== Spinal Nerves === | |||
* [[Nerve | Each [[spinal nerve]] is formed by the union of a [[dorsal root]] and a [[ventral root]]. The ventral root contains the axons of lower motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscles. Damage to these neurons or their axons can lead to the clinical features of a lower motor neuron lesion. | ||
* | == Clinical Features == | ||
Lower motor neuron lesions are characterized by several key clinical features: | |||
==Treatment== | * '''Muscle Weakness''': Due to the loss of innervation, affected muscles become weak. | ||
Treatment | * '''Muscle Atrophy''': Prolonged denervation leads to muscle wasting. | ||
* [[Physical | * '''Fasciculations''': Involuntary muscle twitches may occur due to spontaneous depolarization of motor units. | ||
* Medications | * '''Hypotonia''': Reduced muscle tone is often observed. | ||
* [[ | * '''Hyporeflexia or Areflexia''': Deep tendon reflexes are diminished or absent. | ||
== Causes == | |||
Lower motor neuron lesions can result from a variety of causes, including: | |||
* [[Trauma]]: Injury to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves. | |||
* [[Infection]]: Diseases such as [[poliomyelitis]] can damage lower motor neurons. | |||
* [[Degenerative diseases]]: Conditions like [[amyotrophic lateral sclerosis]] (ALS) affect motor neurons. | |||
==See | * [[Tumors]]: Neoplasms can compress or invade motor neuron pathways. | ||
* [[ | * [[Vascular disorders]]: Ischemia or hemorrhage affecting the spinal cord or brainstem. | ||
* [[ | == Diagnosis == | ||
* [[ | The diagnosis of a lower motor neuron lesion involves clinical examination and may be supported by diagnostic tests such as: | ||
* [[Electromyography]] (EMG): To assess the electrical activity of muscles. | |||
* [[Nerve conduction studies]]: To evaluate the function of peripheral nerves. | |||
* [[Magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI): To visualize the spinal cord and brainstem. | |||
== Treatment == | |||
Treatment of lower motor neuron lesions depends on the underlying cause. Management may include: | |||
* [[Physical therapy]]: To maintain muscle strength and prevent contractures. | |||
* [[Occupational therapy]]: To assist with daily activities. | |||
* [[Medications]]: To manage symptoms such as pain or spasticity. | |||
* [[Surgical intervention]]: In cases of compressive lesions or trauma. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Upper motor neuron lesion]] | |||
* [[Motor neuron disease]] | |||
* [[Peripheral neuropathy]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
[[Category:Motor system]] | |||
[[Category:Motor | |||
Latest revision as of 04:17, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Lower motor neuron lesion | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, fasciculations, hypotonia, areflexia |
| Complications | Paralysis, muscle wasting |
| Onset | Varies depending on cause |
| Duration | Can be chronic or acute |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, infection, autoimmune disease, genetic disorders |
| Risks | Injury, viral infections, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, electromyography, nerve conduction studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Upper motor neuron lesion, myopathy, neuropathy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, occupational therapy, medications |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; depends on underlying cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in certain conditions like spinal muscular atrophy |
| Deaths | N/A |
A lower motor neuron lesion refers to damage or dysfunction of the lower motor neurons (LMNs), which are responsible for transmitting signals from the upper motor neurons to the skeletal muscles. These neurons are located in the anterior horn of the spinal cord and the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem. Lower motor neuron lesions can result in a variety of clinical manifestations, including muscle weakness, atrophy, and diminished reflexes.
Anatomy of Lower Motor Neurons[edit]
Lower motor neurons originate in the central nervous system but extend their axons into the peripheral nervous system. They are the final common pathway for motor commands that initiate voluntary movement. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and in the motor nuclei of cranial nerves.
Spinal Nerves[edit]
Each spinal nerve is formed by the union of a dorsal root and a ventral root. The ventral root contains the axons of lower motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscles. Damage to these neurons or their axons can lead to the clinical features of a lower motor neuron lesion.
Clinical Features[edit]
Lower motor neuron lesions are characterized by several key clinical features:
- Muscle Weakness: Due to the loss of innervation, affected muscles become weak.
- Muscle Atrophy: Prolonged denervation leads to muscle wasting.
- Fasciculations: Involuntary muscle twitches may occur due to spontaneous depolarization of motor units.
- Hypotonia: Reduced muscle tone is often observed.
- Hyporeflexia or Areflexia: Deep tendon reflexes are diminished or absent.
Causes[edit]
Lower motor neuron lesions can result from a variety of causes, including:
- Trauma: Injury to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves.
- Infection: Diseases such as poliomyelitis can damage lower motor neurons.
- Degenerative diseases: Conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) affect motor neurons.
- Tumors: Neoplasms can compress or invade motor neuron pathways.
- Vascular disorders: Ischemia or hemorrhage affecting the spinal cord or brainstem.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of a lower motor neuron lesion involves clinical examination and may be supported by diagnostic tests such as:
- Electromyography (EMG): To assess the electrical activity of muscles.
- Nerve conduction studies: To evaluate the function of peripheral nerves.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): To visualize the spinal cord and brainstem.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of lower motor neuron lesions depends on the underlying cause. Management may include:
- Physical therapy: To maintain muscle strength and prevent contractures.
- Occupational therapy: To assist with daily activities.
- Medications: To manage symptoms such as pain or spasticity.
- Surgical intervention: In cases of compressive lesions or trauma.