Ribonucleotide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ribonucleotide General.png|Ribonucleotide General Structure | |||
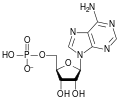
File:AMP structure.svg|AMP Structure | |||
File:GMP chemical structure.png|GMP Chemical Structure | |||
File:Uridinmonophosphat protoniert.svg|Uridine Monophosphate Structure | |||
File:CMP chemical structure.png|CMP Chemical Structure | |||
File:Nucleotides syn1.svg|Nucleotide Synthesis Diagram 1 | |||
File:Nucleotide synthesis.svg|Nucleotide Synthesis | |||
File:Nucleotides syn2.png|Nucleotide Synthesis Diagram 2 | |||
File:Levene.jpg|Portrait of Phoebus Levene | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:18, 20 February 2025
Ribonucleotide is a type of nucleotide that contains ribose as its pentose sugar component. It is considered a fundamental building block of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid), which is essential for all forms of life. Ribonucleotides also play a role in various biological functions such as cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme production.
Structure[edit]
A ribonucleotide is composed of three components: a nitrogenous base, a ribose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. The nitrogenous base can be either a purine (adenine or guanine) or a pyrimidine (cytosine or uracil). The ribose sugar is a five-carbon sugar, and the phosphate group is attached to the 5' carbon of the ribose.
Function[edit]
Ribonucleotides are the building blocks of RNA. They are linked together by phosphodiester bonds to form the backbone of the RNA strand. The sequence of ribonucleotides in an RNA molecule encodes genetic information, which can be translated into proteins by the cell's machinery.
In addition to their role in RNA, ribonucleotides also serve as cofactors for certain enzymes, participate in cell signaling as part of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP, and contribute to the energy metabolism of the cell in the form of ATP and GTP.
Synthesis[edit]
Ribonucleotides are synthesized in the cell through a process called nucleotide synthesis. This process can occur through two pathways: the de novo pathway, which synthesizes ribonucleotides from simple precursors, and the salvage pathway, which recycles free bases and nucleosides that are produced during the degradation of RNA and DNA.
See also[edit]
|
|
|
-
Ribonucleotide General Structure
-
AMP Structure
-
GMP Chemical Structure
-
Uridine Monophosphate Structure
-
CMP Chemical Structure
-
Nucleotide Synthesis Diagram 1
-
Nucleotide Synthesis
-
Nucleotide Synthesis Diagram 2
-
Portrait of Phoebus Levene