Sinus node dysfunction: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Sinus node dysfunction | |||
| image = [[File:ECG_Sinus_Pause.jpg|left|thumb|ECG showing sinus pause]] | |||
| caption = ECG showing sinus pause | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]] | |||
| synonyms = Sick sinus syndrome, sinus node disease | |||
| symptoms = [[Bradycardia]], [[fatigue]], [[dizziness]], [[syncope]] | |||
| complications = [[Heart failure]], [[stroke]] | |||
| onset = Typically in older adults | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Fibrosis]] of the [[sinoatrial node]], [[ischemic heart disease]], [[medications]] | |||
| risks = [[Age]], [[hypertension]], [[diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Electrocardiogram]] (ECG), [[Holter monitor]] | |||
| differential = [[Atrioventricular block]], [[atrial fibrillation]] | |||
| treatment = [[Pacemaker]] implantation, [[medication]] adjustment | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on underlying cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in older adults | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Brady-tachy_syndrome_AV-junctional_rhythm.png|Brady-tachy syndrome with AV junctional rhythm|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Brady-tachy_syndrome_atrial_fibrillation.png|Brady-tachy syndrome with atrial fibrillation|thumb]] | |||
[[File:ECG_Sinus_Bradycardia_49_bpm.jpg|Sinus bradycardia at 49 bpm|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Sinus node dysfunction''' (SND), also known as '''sick sinus syndrome''' (SSS), is a group of heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) in which the heart's natural pacemaker (sinus node) doesn't work properly. The sinus node is an area of specialized cells in the upper right chamber of the heart that controls the rhythm of your heart. Normally, the sinus node produces a steady pace of regular electrical impulses. In sick sinus syndrome, these signals are abnormally paced. | '''Sinus node dysfunction''' (SND), also known as '''sick sinus syndrome''' (SSS), is a group of heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) in which the heart's natural pacemaker (sinus node) doesn't work properly. The sinus node is an area of specialized cells in the upper right chamber of the heart that controls the rhythm of your heart. Normally, the sinus node produces a steady pace of regular electrical impulses. In sick sinus syndrome, these signals are abnormally paced. | ||
A person with sinus node dysfunction may have heart rhythms that are too fast, too slow, punctuated by long pauses — or an alternating combination of all of these rhythm problems. Sinus node dysfunction is relatively uncommon, but the risk of developing it increases with age. Many people with sinus node dysfunction eventually need a pacemaker to keep the heart in a regular rhythm. | |||
A person with sinus node dysfunction may have heart rhythms that are too fast, too slow, punctuated by long pauses | |||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Sinus node dysfunction often doesn't cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may mimic those caused by other health problems, making the condition difficult to diagnose. Symptoms may include: | Sinus node dysfunction often doesn't cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may mimic those caused by other health problems, making the condition difficult to diagnose. Symptoms may include: | ||
| Line 13: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Trouble sleeping]] or staying asleep | * [[Trouble sleeping]] or staying asleep | ||
* [[Confusion]] or difficulty remembering things | * [[Confusion]] or difficulty remembering things | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Sinus node dysfunction is associated with damage to or degeneration of the sinus node | Sinus node dysfunction is associated with damage to or degeneration of the sinus node — often the result of underlying conditions or medical treatments. Conditions that can cause or contribute to problems with the sinus node include: | ||
* [[Aging]] | * [[Aging]] | ||
* [[Heart disease]] | * [[Heart disease]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 41: | ||
* [[Hyperkalemia]] (high potassium levels) | * [[Hyperkalemia]] (high potassium levels) | ||
* Previous heart surgery near the sinus node | * Previous heart surgery near the sinus node | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for sinus node dysfunction usually involves addressing underlying health problems and reducing symptoms. If symptoms are severe or the condition is causing more serious heart rhythm problems, treatment may involve medications to control the heart rate or the implantation of a pacemaker. | Treatment for sinus node dysfunction usually involves addressing underlying health problems and reducing symptoms. If symptoms are severe or the condition is causing more serious heart rhythm problems, treatment may involve medications to control the heart rate or the implantation of a pacemaker. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Arrhythmia]] | * [[Arrhythmia]] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 48: | ||
* [[Tachycardia]] | * [[Tachycardia]] | ||
* [[Pacemaker]] | * [[Pacemaker]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Heart diseases]] | [[Category:Heart diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:58, 13 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Sinus node dysfunction | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Sick sinus syndrome, sinus node disease |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Bradycardia, fatigue, dizziness, syncope |
| Complications | Heart failure, stroke |
| Onset | Typically in older adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Fibrosis of the sinoatrial node, ischemic heart disease, medications |
| Risks | Age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus |
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor |
| Differential diagnosis | Atrioventricular block, atrial fibrillation |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Pacemaker implantation, medication adjustment |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on underlying cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in older adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
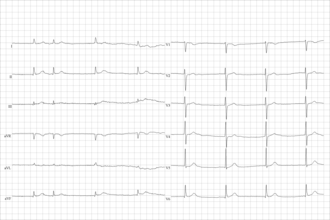
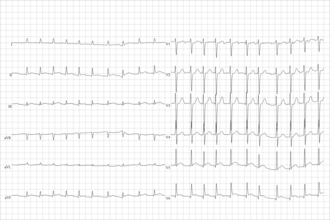
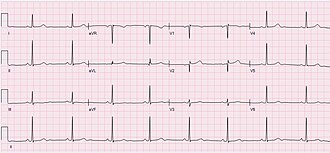
Sinus node dysfunction (SND), also known as sick sinus syndrome (SSS), is a group of heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) in which the heart's natural pacemaker (sinus node) doesn't work properly. The sinus node is an area of specialized cells in the upper right chamber of the heart that controls the rhythm of your heart. Normally, the sinus node produces a steady pace of regular electrical impulses. In sick sinus syndrome, these signals are abnormally paced. A person with sinus node dysfunction may have heart rhythms that are too fast, too slow, punctuated by long pauses — or an alternating combination of all of these rhythm problems. Sinus node dysfunction is relatively uncommon, but the risk of developing it increases with age. Many people with sinus node dysfunction eventually need a pacemaker to keep the heart in a regular rhythm.
Symptoms[edit]
Sinus node dysfunction often doesn't cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may mimic those caused by other health problems, making the condition difficult to diagnose. Symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting or near fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pains
- Trouble sleeping or staying asleep
- Confusion or difficulty remembering things
Causes[edit]
Sinus node dysfunction is associated with damage to or degeneration of the sinus node — often the result of underlying conditions or medical treatments. Conditions that can cause or contribute to problems with the sinus node include:
- Aging
- Heart disease
- Medications, including some drugs for heart rhythm disorders, high blood pressure and psychiatric problems
- Sleep apnea
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels)
- Previous heart surgery near the sinus node
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for sinus node dysfunction usually involves addressing underlying health problems and reducing symptoms. If symptoms are severe or the condition is causing more serious heart rhythm problems, treatment may involve medications to control the heart rate or the implantation of a pacemaker.


