Leukocoria: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Leukocoria | |||
| image = [[File:Rb_whiteeye.PNG|left|thumb|Leukocoria in a child with retinoblastoma]] | |||
| caption = Leukocoria in a child with [[retinoblastoma]] | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| symptoms = Abnormal white reflection from the [[retina]] | |||
| complications = [[Blindness]], [[retinal detachment]] | |||
| onset = Can be present at birth or develop later | |||
| duration = Varies depending on underlying cause | |||
| causes = [[Retinoblastoma]], [[congenital cataract]], [[Coats' disease]], [[persistent fetal vasculature]], [[retinopathy of prematurity]] | |||
| risks = Family history of [[retinoblastoma]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ophthalmoscopy]], [[ultrasound]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Cataract]], [[retinal detachment]], [[vitreous hemorrhage]] | |||
| treatment = Depends on underlying cause; may include [[surgery]], [[chemotherapy]], [[radiation therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; early detection and treatment improve outcomes | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Fundus_retinoblastoma.jpg|Retinoblastoma|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Leukocoria''' (also known as '''white pupillary reflex''') is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. It is a medical sign for a number of conditions, primarily those affecting the retina or cornea, and is often detected in flash photography. | '''Leukocoria''' (also known as '''white pupillary reflex''') is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. It is a medical sign for a number of conditions, primarily those affecting the retina or cornea, and is often detected in flash photography. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Leukocoria can be caused by a number of conditions, including: | Leukocoria can be caused by a number of conditions, including: | ||
* [[Retinoblastoma]]: A rare type of eye cancer that usually develops in early childhood, typically before the age of 5. | * [[Retinoblastoma]]: A rare type of eye cancer that usually develops in early childhood, typically before the age of 5. | ||
* [[Coats' disease]]: A rare condition characterized by abnormal development of the blood vessels in the retina. | * [[Coats' disease]]: A rare condition characterized by abnormal development of the blood vessels in the retina. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 26: | ||
* [[Cataract]]: A clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. | * [[Cataract]]: A clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. | ||
* [[Retinopathy of prematurity]] (ROP): A potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants. | * [[Retinopathy of prematurity]] (ROP): A potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of leukocoria is typically made through a comprehensive eye examination. This may include: | Diagnosis of leukocoria is typically made through a comprehensive eye examination. This may include: | ||
* [[Visual acuity test]]: This test measures how well the patient sees at various distances. | * [[Visual acuity test]]: This test measures how well the patient sees at various distances. | ||
* [[Dilated eye exam]]: Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve. | * [[Dilated eye exam]]: Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve. | ||
* [[Tonometry]]: An instrument measures the pressure inside the eye to check for glaucoma. | * [[Tonometry]]: An instrument measures the pressure inside the eye to check for glaucoma. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for leukocoria depends on the underlying cause and may include surgery, chemotherapy, laser therapy, or cryotherapy. | Treatment for leukocoria depends on the underlying cause and may include surgery, chemotherapy, laser therapy, or cryotherapy. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Eye examination]] | * [[Eye examination]] | ||
* [[Pediatric ophthalmology]] | * [[Pediatric ophthalmology]] | ||
* [[Retinal diseases]] | * [[Retinal diseases]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Medical signs]] | [[Category:Medical signs]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatric disorders]] | [[Category:Pediatric disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:02, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Leukocoria | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abnormal white reflection from the retina |
| Complications | Blindness, retinal detachment |
| Onset | Can be present at birth or develop later |
| Duration | Varies depending on underlying cause |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Retinoblastoma, congenital cataract, Coats' disease, persistent fetal vasculature, retinopathy of prematurity |
| Risks | Family history of retinoblastoma |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Cataract, retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Depends on underlying cause; may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; early detection and treatment improve outcomes |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
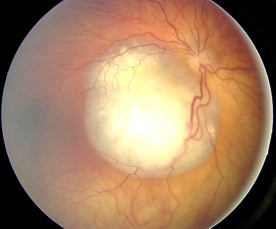
Leukocoria (also known as white pupillary reflex) is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. It is a medical sign for a number of conditions, primarily those affecting the retina or cornea, and is often detected in flash photography.
Causes[edit]
Leukocoria can be caused by a number of conditions, including:
- Retinoblastoma: A rare type of eye cancer that usually develops in early childhood, typically before the age of 5.
- Coats' disease: A rare condition characterized by abnormal development of the blood vessels in the retina.
- Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV): A rare condition in which the blood vessels and fibrous tissue behind the lens of the eye do not regress normally during fetal development.
- Cataract: A clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision.
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP): A potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of leukocoria is typically made through a comprehensive eye examination. This may include:
- Visual acuity test: This test measures how well the patient sees at various distances.
- Dilated eye exam: Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve.
- Tonometry: An instrument measures the pressure inside the eye to check for glaucoma.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for leukocoria depends on the underlying cause and may include surgery, chemotherapy, laser therapy, or cryotherapy.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />


