Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
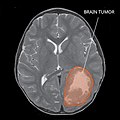
'''Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor''' (CNS PNET) is a rare and highly aggressive [[cancer]] that primarily affects children and young adults. It is a type of [[neuroectodermal tumor]] that originates from the [[neural crest]] cells in the [[central nervous system]]. | {{SI}} {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor | |||
| image = [[File:PNET.jpg|alt=Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor|upright=1.2]] | |||
| caption = MRI of a central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = CNS PNET | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[seizures]], [[neurological deficits]] | |||
| complications = [[Hydrocephalus]], [[metastasis]] | |||
| onset = Typically in [[children]] and [[young adults]] | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| types = [[Medulloblastoma]], [[pineoblastoma]], [[ependymoblastoma]] | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[radiation exposure]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Medulloblastoma]], [[atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor]], [[ependymoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on type and stage | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = Varies | |||
}}'''Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor''' (CNS PNET) is a rare and highly aggressive [[cancer]] that primarily affects children and young adults. It is a type of [[neuroectodermal tumor]] that originates from the [[neural crest]] cells in the [[central nervous system]]. | |||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
CNS PNETs are classified as [[embryonal tumors]], a category of [[neoplasms]] that also includes [[medulloblastoma]] and [[atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor]] (ATRT). They are further classified based on their location in the brain, with the most common types being cerebral, pineal, and spinal. | CNS PNETs are classified as [[embryonal tumors]], a category of [[neoplasms]] that also includes [[medulloblastoma]] and [[atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor]] (ATRT). They are further classified based on their location in the brain, with the most common types being cerebral, pineal, and spinal. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of CNS PNETs vary depending on the location of the tumor. Common symptoms include [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and changes in behavior or personality. In some cases, the tumor may cause [[seizures]] or [[neurological deficits]]. | The symptoms of CNS PNETs vary depending on the location of the tumor. Common symptoms include [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and changes in behavior or personality. In some cases, the tumor may cause [[seizures]] or [[neurological deficits]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of CNS PNETs typically involves a combination of [[neuroimaging]] techniques, such as [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) and [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans, and [[biopsy]] to confirm the diagnosis. [[Histopathology]] and [[immunohistochemistry]] are also used to differentiate CNS PNETs from other types of brain tumors. | Diagnosis of CNS PNETs typically involves a combination of [[neuroimaging]] techniques, such as [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) and [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans, and [[biopsy]] to confirm the diagnosis. [[Histopathology]] and [[immunohistochemistry]] are also used to differentiate CNS PNETs from other types of brain tumors. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for CNS PNETs usually involves a combination of [[surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], and [[chemotherapy]]. The goal of treatment is to remove as much of the tumor as possible and to kill any remaining cancer cells. Despite aggressive treatment, the prognosis for CNS PNETs is generally poor, with a five-year survival rate of less than 50%. | Treatment for CNS PNETs usually involves a combination of [[surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], and [[chemotherapy]]. The goal of treatment is to remove as much of the tumor as possible and to kill any remaining cancer cells. Despite aggressive treatment, the prognosis for CNS PNETs is generally poor, with a five-year survival rate of less than 50%. | ||
== Research == | == Research == | ||
Research into CNS PNETs is ongoing, with a focus on understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms that drive these tumors. This research may lead to the development of new treatments and improve the prognosis for individuals with this disease. | Research into CNS PNETs is ongoing, with a focus on understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms that drive these tumors. This research may lead to the development of new treatments and improve the prognosis for individuals with this disease. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Medulloepithelioma_Histology.jpg|Histology of Medulloepithelioma | |||
File:Ependymoblastomatous_Rosette.jpg|Ependymoblastomatous Rosette | |||
File:MRI_of_PNET.jpg|MRI of Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Neoplasms]] | [[Category:Neoplasms]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatric cancers]] | [[Category:Pediatric cancers]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 42: | ||
{{Cancer-stub}} | {{Cancer-stub}} | ||
{{Neuroscience-stub}} | {{Neuroscience-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:18, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor | |
|---|---|
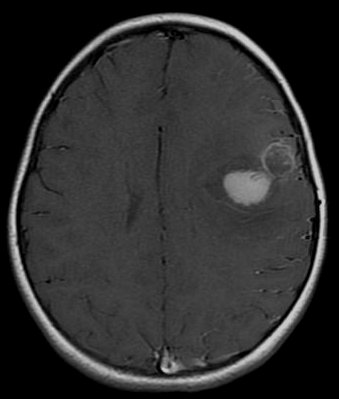
| |
| Synonyms | CNS PNET |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, seizures, neurological deficits |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, metastasis |
| Onset | Typically in children and young adults |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Medulloblastoma, pineoblastoma, ependymoblastoma |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, radiation exposure |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Medulloblastoma, atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor, ependymoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on type and stage |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | Varies |
Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor (CNS PNET) is a rare and highly aggressive cancer that primarily affects children and young adults. It is a type of neuroectodermal tumor that originates from the neural crest cells in the central nervous system.
Classification[edit]
CNS PNETs are classified as embryonal tumors, a category of neoplasms that also includes medulloblastoma and atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (ATRT). They are further classified based on their location in the brain, with the most common types being cerebral, pineal, and spinal.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of CNS PNETs vary depending on the location of the tumor. Common symptoms include headache, nausea, vomiting, and changes in behavior or personality. In some cases, the tumor may cause seizures or neurological deficits.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of CNS PNETs typically involves a combination of neuroimaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, and biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry are also used to differentiate CNS PNETs from other types of brain tumors.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for CNS PNETs usually involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The goal of treatment is to remove as much of the tumor as possible and to kill any remaining cancer cells. Despite aggressive treatment, the prognosis for CNS PNETs is generally poor, with a five-year survival rate of less than 50%.
Research[edit]
Research into CNS PNETs is ongoing, with a focus on understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms that drive these tumors. This research may lead to the development of new treatments and improve the prognosis for individuals with this disease.
Gallery[edit]
-
Histology of Medulloepithelioma
-
Ependymoblastomatous Rosette
-
MRI of Central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!