Entamoeba histolytica: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Infectious diseases}} | {{Infectious diseases}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_trophozoite.png|Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_in_blood.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica in blood | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_life_cycle-en.svg|Entamoeba histolytica life cycle | |||
File:Amoebic_Ulcer_Intestine.jpg|Amoebic Ulcer Intestine | |||
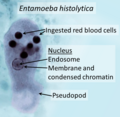
File:Trophozoites_of_Entamoeba_histolytica_with_ingested_erythrocytes.JPG|Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with ingested erythrocytes | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_01.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica | |||
File:Ehistdisp_cyst_wtmt.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica cyst | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_quadrinucleate_cyst.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica quadrinucleate cyst | |||
File:Entamoeba_histolytica_binary_fission.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica binary fission | |||
File:Entamoeba_hystolytica.jpg|Entamoeba histolytica | |||
File:Immunohistochemical_staining_of_trophozoites_(brown)_using_specific_anti–Entamoeba_histolytica_macrophage_migration_inhibitory_factor_antibodies_in_a_patient_with_amebic_colitis.jpg|Immunohistochemical staining of trophozoites using specific anti–Entamoeba histolytica antibodies | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:53, 18 February 2025
Entamoeba histolytica is a protozoan parasite responsible for a disease known as amoebiasis. This single-celled organism primarily infects humans and other primates. Although it is found worldwide, it is most prevalent in tropical regions with poor sanitary conditions.
Life Cycle[edit]
The life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica involves two stages: the trophozoite and the cyst. The trophozoite is the active, feeding, and dividing stage, while the cyst is the dormant, non-feeding, and infective stage. The cysts are excreted in the feces of an infected individual and can survive in the environment for weeks. If ingested by another individual, the cysts transform into trophozoites in the small intestine and then migrate to the large intestine.
Pathogenesis[edit]
Entamoeba histolytica causes disease by invading the intestinal wall, causing ulceration and inflammation. In severe cases, the amoebae can penetrate the intestinal wall and spread to other organs, primarily the liver, causing amoebic liver abscess.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of Entamoeba histolytica infection is made by identifying the parasite in stool samples. Treatment typically involves antiprotozoal drugs such as metronidazole.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of Entamoeba histolytica infection primarily involves improved sanitation and hygiene practices, including proper disposal of human feces, protection of food and water supplies from contamination, and careful handwashing.
See Also[edit]
| Parasites | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This parasitology-related article is a stub.
|
| Protozoa | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Tropical diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This Tropical disease related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
|
| Infectious diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This infectious diseases related article is a stub.
|
-
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite
-
Entamoeba histolytica in blood
-
Entamoeba histolytica life cycle
-
Amoebic Ulcer Intestine
-
Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with ingested erythrocytes
-
Entamoeba histolytica
-
Entamoeba histolytica cyst
-
Entamoeba histolytica quadrinucleate cyst
-
Entamoeba histolytica binary fission
-
Entamoeba histolytica
-
Immunohistochemical staining of trophozoites using specific anti–Entamoeba histolytica antibodies