Parasitic disease

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Parasitic disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Varies by parasite; may include fever, fatigue, gastrointestinal symptoms, skin rash |
| Complications | Anemia, malnutrition, organ damage |
| Onset | Varies by parasite |
| Duration | Acute or chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Parasites such as protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites |
| Risks | Poor sanitation, lack of clean water, exposure to vectors |
| Diagnosis | Microscopy, serology, molecular diagnostics |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Vector control, sanitation, prophylactic medication |
| Treatment | Antiparasitic drugs, supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in tropical and subtropical regions |
| Deaths | N/A |
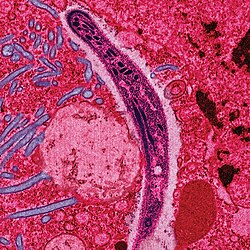
A disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes
Parasitic diseases are infections caused by parasites, which are organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive their nutrients at the host's expense. One of the most well-known parasitic diseases is malaria, caused by the Plasmodium parasite and transmitted by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Types of Parasitic Diseases[edit]
Parasitic diseases can be classified into three main types based on the type of parasite:
Protozoan Infections[edit]
Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can cause diseases such as malaria, amoebiasis, and giardiasis. Malaria, in particular, is a significant global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions.
Helminth Infections[edit]
Helminths are multicellular parasitic worms, including roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes. These parasites can cause diseases such as schistosomiasis, ascariasis, and hookworm infection.
Ectoparasitic Infections[edit]
Ectoparasites live on the surface of the host and include organisms such as lice, fleas, and mites. They can cause conditions like scabies and pediculosis.
Transmission[edit]
Parasitic diseases are transmitted through various routes, including:
- Vector-borne transmission: As seen in malaria, where mosquitoes act as vectors.
- Fecal-oral transmission: Common in protozoan infections like amoebiasis.
- Direct contact: Seen in ectoparasitic infections like scabies.
- Consumption of contaminated food or water: A route for many helminth infections.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of parasitic diseases vary widely depending on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills (common in malaria)
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea (common in amoebiasis and giardiasis)
- Skin rashes and itching (common in scabies)
- Fatigue and weight loss (common in helminth infections)
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of parasitic diseases often involves:
- Microscopic examination: Identifying parasites in blood, stool, or tissue samples.
- Serological tests: Detecting antibodies or antigens related to the parasite.
- Molecular methods: Using PCR to detect parasite DNA.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment depends on the specific parasite involved and may include:
- Antimalarial drugs: Such as chloroquine or artemisinin-based combination therapies for malaria.
- Antiprotozoal medications: Such as metronidazole for amoebiasis.
- Anthelmintic drugs: Such as albendazole or mebendazole for helminth infections.
- Topical treatments: For ectoparasitic infections like scabies.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures include:
- Vector control: Using insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying to prevent malaria.
- Improved sanitation: To prevent fecal-oral transmission of parasites.
- Health education: Promoting hygiene and safe food practices.
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
Error creating thumbnail: ![]() Error creating thumbnail:
Error creating thumbnail:
![]()
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian