C-Met inhibitor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
File:Tivantinib.svg|C-Met_inhibitor | File:Tivantinib.svg|C-Met_inhibitor | ||
File:Current_status_in_c-met_inhibitors_2010.tif|C-Met_inhibitor | File:Current_status_in_c-met_inhibitors_2010.tif|C-Met_inhibitor | ||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:K252_and_c-met.png|K252 and c-Met | |||
File:SU_11274.tif|SU 11274 | |||
File:PHA_665752.tif|PHA 665752 | |||
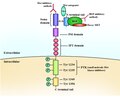
File:RTK_scematic_labelled.tif|RTK Schematic Labelled | |||
File:RTK_domain.jpg|RTK Domain | |||
File:Class_I_c-met_inhibitors_analogs.tif|Class I c-Met Inhibitors Analogs | |||
File:MK2461.tif|MK2461 | |||
File:Class_II_c-met_inhibitors_analogs.tif|Class II c-Met Inhibitors Analogs | |||
File:Tivantinib.svg|Tivantinib | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 18 February 2025
C-Met inhibitor is a type of drug that is used in the treatment of cancer. It works by blocking the activity of the C-Met protein, which is often overactive in certain types of cancer cells. This overactivity can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and the spread of cancer.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
C-Met inhibitors work by binding to the C-Met protein, which is a receptor tyrosine kinase. This binding prevents the protein from activating, which in turn prevents the cell from receiving signals to grow and divide. This can slow or stop the growth of cancer cells that rely on C-Met for their growth.
Uses[edit]
C-Met inhibitors are used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including lung cancer, gastric cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. They are often used when other treatments have failed or when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all drugs, C-Met inhibitors can cause side effects. These can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. In some cases, they can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or heart problems.
Examples[edit]
There are several different C-Met inhibitors that are currently in use or in clinical trials. These include crizotinib, capmatinib, and tepotinib.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
C-Met_inhibitor
-
K252 and c-Met
-
SU 11274
-
PHA 665752
-
RTK Schematic Labelled
-
RTK Domain
-
Class I c-Met Inhibitors Analogs
-
MK2461
-
Class II c-Met Inhibitors Analogs
-
Tivantinib