Trimethoprim: Difference between revisions
m Text replacement - "Category:Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate" to "" |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477241123 | |||
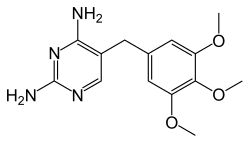
| image = Trimethoprim.svg | |||
| image2 = Trimethoprim-from-hydrochloride-xtal-1984-3D-balls.png | |||
| image3 = Wild-type_staphylococcus_aureus_DHFR_in_complex_with_NADPH_and_trimethoprim.gif | |||
}} | |||
'''Trimethoprim''' is an [[antibiotic]] used primarily in the treatment of [[urinary tract infection]]s, although it is also used for other types of bacterial infections. It is often used in combination with [[sulfamethoxazole]] as [[co-trimoxazole]]. | |||
Trimethoprim is used | |||
==Mechanism of action== | |||
Trimethoprim works by inhibiting the bacterial [[enzyme]] [[dihydrofolate reductase]], which is involved in the synthesis of [[tetrahydrofolate]], a form of [[folic acid]] that bacteria need to produce [[DNA]], [[RNA]], and [[proteins]]. By blocking this enzyme, trimethoprim effectively halts bacterial growth. | |||
[[File:THFsynthesispathway.png|thumb|right|Diagram of the tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway.]] | |||
==Uses== | |||
Trimethoprim is primarily used to treat [[urinary tract infection]]s, but it is also effective against other types of infections such as [[respiratory tract infection]]s and [[traveler's diarrhea]]. It is often used in combination with sulfamethoxazole to enhance its antibacterial effect. | |||
==Side effects== | ==Side effects== | ||
Common side effects of trimethoprim include [[nausea]], | Common side effects of trimethoprim include [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and [[rash]]. More serious side effects can include [[bone marrow suppression]], which can lead to [[anemia]], [[leukopenia]], and [[thrombocytopenia]]. | ||
== | ==Resistance== | ||
Bacterial resistance to trimethoprim can occur through various mechanisms, including the production of an altered dihydrofolate reductase enzyme that is not inhibited by the drug. Resistance is a growing concern, particularly in the treatment of urinary tract infections. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Trimethoprim was first used in | Trimethoprim was first synthesized in the 1960s and was introduced into clinical use in the 1970s. It has since become a widely used antibiotic, particularly in combination with sulfamethoxazole. | ||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Antibiotic]] | |||
* [[Urinary tract infection]] | |||
* [[Sulfamethoxazole]] | |||
* [[Co-trimoxazole]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Antibiotics]] | [[Category:Antibiotics]] | ||
[[Category:Antifolate]] | |||
[[Category:World Health Organization essential medicines]] | [[Category:World Health Organization essential medicines]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Trimethoprim.svg|Chemical structure of Trimethoprim | |||
File:Trimethoprim-from-hydrochloride-xtal-1984-3D-balls.png|3D ball model of Trimethoprim from hydrochloride crystal | |||
File:Wild-type_staphylococcus_aureus_DHFR_in_complex_with_NADPH_and_trimethoprim.gif|Wild-type Staphylococcus aureus DHFR in complex with NADPH and Trimethoprim | |||
File:THFsynthesispathway.png|Tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:30, 18 February 2025
Antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections
| Trimethoprim | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Trimethoprim is an antibiotic used primarily in the treatment of urinary tract infections, although it is also used for other types of bacterial infections. It is often used in combination with sulfamethoxazole as co-trimoxazole.
Mechanism of action[edit]
Trimethoprim works by inhibiting the bacterial enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved in the synthesis of tetrahydrofolate, a form of folic acid that bacteria need to produce DNA, RNA, and proteins. By blocking this enzyme, trimethoprim effectively halts bacterial growth.

Uses[edit]
Trimethoprim is primarily used to treat urinary tract infections, but it is also effective against other types of infections such as respiratory tract infections and traveler's diarrhea. It is often used in combination with sulfamethoxazole to enhance its antibacterial effect.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of trimethoprim include nausea, vomiting, and rash. More serious side effects can include bone marrow suppression, which can lead to anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Resistance[edit]
Bacterial resistance to trimethoprim can occur through various mechanisms, including the production of an altered dihydrofolate reductase enzyme that is not inhibited by the drug. Resistance is a growing concern, particularly in the treatment of urinary tract infections.
History[edit]
Trimethoprim was first synthesized in the 1960s and was introduced into clinical use in the 1970s. It has since become a widely used antibiotic, particularly in combination with sulfamethoxazole.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Chemical structure of Trimethoprim
-
3D ball model of Trimethoprim from hydrochloride crystal
-
Wild-type Staphylococcus aureus DHFR in complex with NADPH and Trimethoprim
-
Tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway



