Zygomycosis

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Zygomycosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Mucormycosis, Phycomycosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
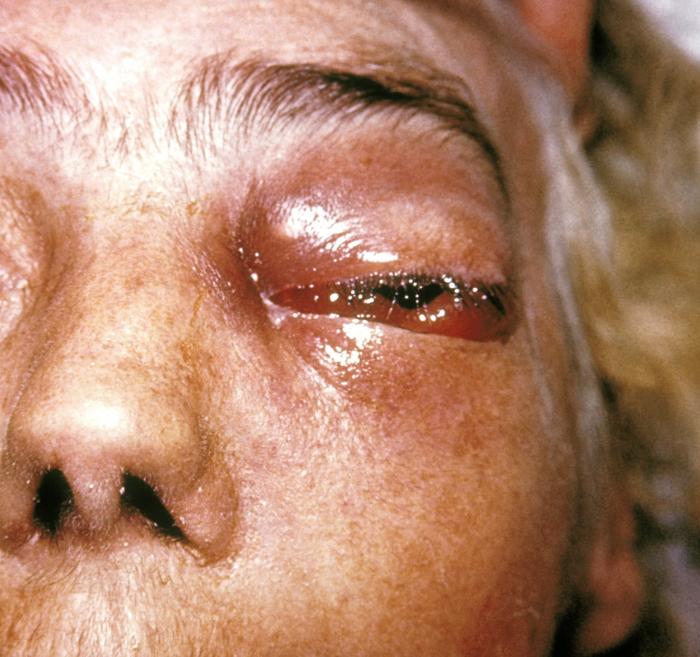
| Symptoms | Fever, headache, facial swelling, nasal congestion, black lesions on nasal bridge or upper inside of mouth |
| Complications | Tissue necrosis, blindness, cerebral infarction, death |
| Onset | Rapid |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Fungal infection by Mucorales |
| Risks | Diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression, iron overload, trauma, burns |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, culture, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Bacterial sinusitis, aspergillosis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Antifungal medication, surgical debridement |
| Medication | Amphotericin B, posaconazole, isavuconazole |
| Prognosis | Poor if untreated |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Error creating thumbnail:
Zygomycosis, also known as mucormycosis, is a serious fungal infection caused by fungi in the order Mucorales. This rare but potentially life-threatening condition primarily affects individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with uncontrolled diabetes, cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, and individuals receiving immunosuppressive drugs.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit]
Zygomycosis is caused by the inhalation of fungal spores from the environment. The fungi responsible for this infection belong to several genera, most notably Rhizopus, Mucor, and Absidia. These fungi are ubiquitous in nature, found in soil, decaying organic matter, and even in the air. While these spores are commonly inhaled by people every day without causing infection, individuals with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing zygomycosis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis[edit]
The symptoms of zygomycosis vary depending on the part of the body affected. The infection can manifest in several forms, including rhinocerebral, pulmonary, cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and disseminated zygomycosis. The most common form, rhinocerebral zygomycosis, begins with symptoms such as fever, nasal congestion, and headaches. As the infection progresses, it can lead to facial swelling, black lesions on the nasal bridge or upper inside of the mouth, and potentially, loss of vision or neurological deficits. Diagnosis of zygomycosis involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Biopsy and culture of the affected tissues are crucial for confirming the presence of the fungi.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of zygomycosis requires an aggressive approach that includes antifungal therapy, surgical debridement of infected tissue, and management of underlying conditions. The primary antifungal medication used is Amphotericin B, although newer agents like posaconazole and isavuconazole have also been used. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for improving outcomes, as the infection can rapidly become fatal if not promptly addressed.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures for zygomycosis are primarily focused on individuals with high-risk conditions. These include controlling diabetes mellitus, reducing the use of immunosuppressive drugs when possible, and employing protective measures in environments with a high concentration of fungal spores.
Epidemiology[edit]
Zygomycosis is a rare infection, with its incidence increasing in recent years, possibly due to the growing number of individuals with compromised immune systems. It has a global distribution, with no specific geographic predilection.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with zygomycosis depends on several factors, including the site of infection, the extent of disease, the patient's immune status, and the timeliness of treatment. Despite aggressive treatment, the mortality rate remains high, especially in cases of disseminated infection.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
