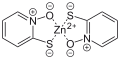
Zinc pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione is an inorganic compound with the formula (C₅H₄NOS)₂Zn. It is a coordination complex where zinc is coordinated by two pyrithione ligands. Zinc pyrithione is best known for its use in treating dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis, as well as its application in antifouling paints. It also exhibits antibacterial, antimicrobial, and antifungal properties, making it a common ingredient in various cosmetic and industrial products.
Uses[edit]
Zinc pyrithione is widely used in shampoos and other cosmetic products to prevent and treat dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Its antifungal properties are effective against the fungus Malassezia, which is believed to contribute to these conditions. Additionally, zinc pyrithione is found in over-the-counter antifungal creams, body washes, and face washes designed to treat a variety of skin conditions.
Beyond personal care products, zinc pyrithione is utilized in the paint industry, particularly in antifouling paints for boats and ships. These paints prevent the growth of marine organisms on the hulls, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Zinc pyrithione's antimicrobial activity is attributed to its ability to disrupt membrane transport by blocking the proton pump that energizes the transport mechanism. This action inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi. For dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis, it reduces the population of Malassezia yeast on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with these conditions.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
While zinc pyrithione is generally considered safe for topical use, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include mild itching, stinging, or burning sensations upon application. Allergic reactions, though rare, can occur and may present as severe itching, redness, swelling, or difficulty breathing. It is important for individuals to discontinue use and seek medical advice if they experience any adverse reactions.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The use of zinc pyrithione in antifouling paints has raised environmental concerns. Its toxicity to marine life can lead to disruptions in aquatic ecosystems, particularly in areas with high concentrations of treated vessels. Regulatory bodies in some regions have implemented restrictions on the use of zinc pyrithione in marine coatings to mitigate its environmental impact.
Regulation[edit]
The concentration of zinc pyrithione in cosmetic products is regulated by health authorities in many countries. For example, the European Union allows a maximum concentration of 0.5% in leave-on hair products and 1% in rinse-off products. These regulations are in place to ensure the safety and efficacy of products containing zinc pyrithione.
Conclusion[edit]
Zinc pyrithione is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications in personal care products and industrial applications. Its antimicrobial properties make it an effective ingredient in treatments for dandruff, seborrhoeic dermatitis, and various skin conditions. However, its use must be balanced with considerations for potential side effects and environmental impact.
-
Zinc pyrithione chemical structure
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian