Warfarin necrosis

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Warfarin necrosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Coumadin necrosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Hematology, Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Skin necrosis, pain, erythema, hemorrhage |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Typically 3-5 days after starting warfarin |
| Duration | Variable, depending on treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Warfarin therapy |
| Risks | Protein C deficiency, Protein S deficiency, high initial doses of warfarin |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, purpura fulminans, calciphylaxis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Discontinuation of warfarin, vitamin K, heparin, fresh frozen plasma, protein C concentrate |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, can be severe if not treated promptly |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Warfarin necrosis is a rare but serious complication associated with the use of the anticoagulant medication warfarin. It is characterized by the development of skin necrosis, which typically occurs within the first few days of starting warfarin therapy. This condition is a result of an imbalance in the coagulation system, leading to excessive clotting in small blood vessels and subsequent tissue death.
Pathophysiology[edit]
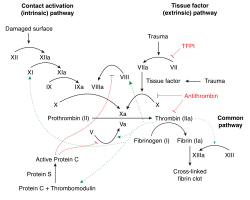
Warfarin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, specifically factors II, VII, IX, and X, as well as proteins C and S. Protein C and Protein S are natural anticoagulants that help regulate the coagulation cascade. When warfarin is initiated, there is a rapid decline in protein C levels due to its shorter half-life compared to the procoagulant factors. This transient hypercoagulable state can lead to the formation of microthrombi in the dermal vasculature, resulting in skin necrosis.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Warfarin necrosis typically presents within 3 to 10 days after the initiation of warfarin therapy. Patients may initially notice pain and erythema in affected areas, which are most commonly the breasts, thighs, buttocks, and abdomen. These areas can rapidly progress to purpura, bullae, and eventually necrosis. The necrotic tissue may become black and escharotic, requiring surgical debridement in severe cases.
Risk Factors[edit]
Several risk factors have been identified for the development of warfarin necrosis, including:
- Female gender
- Obesity
- High initial doses of warfarin
- Deficiency of protein C or protein S
- Previous history of thromboembolic events
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of warfarin necrosis is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic presentation and temporal relationship with the initiation of warfarin therapy. Laboratory tests may reveal a prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and a decrease in protein C and S levels. A skin biopsy can confirm the presence of microvascular thrombosis and necrosis.
Management[edit]
The management of warfarin necrosis involves the immediate discontinuation of warfarin and the administration of alternative anticoagulation, such as heparin. Vitamin K may be given to reverse the effects of warfarin. In cases of protein C deficiency, replacement therapy with protein C concentrate or fresh frozen plasma may be beneficial. Surgical intervention may be necessary for debridement of necrotic tissue.
Prevention[edit]
To prevent warfarin necrosis, it is recommended to start warfarin at a low dose and gradually increase it while overlapping with heparin until the therapeutic range is achieved. Monitoring of protein C and S levels may be considered in high-risk individuals.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian