Tinea nigra

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Tinea nigra | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Keratomycosis nigricans palmaris |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Asymptomatic dark brown or black patches on palms or soles |
| Complications | None |
| Onset | Any age, more common in children and young adults |
| Duration | Chronic if untreated |
| Types | N/A |
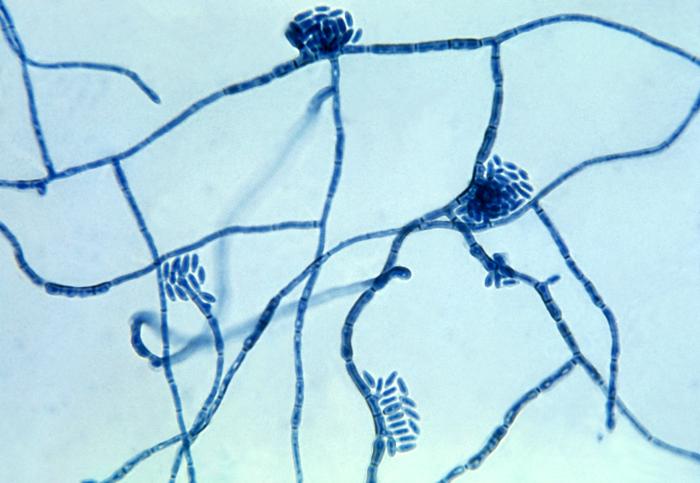
| Causes | Hortaea werneckii |
| Risks | Warm and humid climates |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, KOH test, skin biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Melanoma, nevus, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation |
| Prevention | Avoidance of contaminated soil or water |
| Treatment | Topical antifungals such as miconazole, clotrimazole |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Excellent with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Tinea nigra is a superficial fungal infection of the skin caused by the dematiaceous (darkly pigmented) fungus Hortaea werneckii. This condition is characterized by brown to black, non-scaly patches on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It is a relatively rare infection and is most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Presentation[edit]
The primary symptom of tinea nigra is the appearance of dark patches on the skin. These patches are usually asymptomatic, meaning they do not cause pain or itching. The lesions are typically well-defined, flat, and can vary in color from light brown to black. They are most commonly found on the palms and soles but can occasionally appear on other parts of the body.
Pathogenesis[edit]
Tinea nigra is caused by the fungus Hortaea werneckii, which is a type of dematiaceous fungi. The fungus produces melanin, which gives the lesions their characteristic dark color. The infection is usually acquired through direct contact with contaminated soil, wood, or decaying vegetation. The fungus thrives in warm, humid environments, which is why the infection is more prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of tinea nigra is typically made through clinical examination and confirmed by laboratory tests. A skin scraping from the affected area can be examined under a microscope after being treated with potassium hydroxide (KOH). The presence of darkly pigmented, septate hyphae and yeast-like cells is indicative of Hortaea werneckii. Culture and histopathological examination can also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for tinea nigra is usually straightforward and involves the use of topical antifungal agents. Commonly used medications include miconazole, clotrimazole, and terbinafine. These treatments are typically applied to the affected area once or twice daily for several weeks. In some cases, keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid may be used to help remove the outer layer of skin and enhance the effectiveness of the antifungal treatment.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing tinea nigra involves minimizing exposure to the environmental sources of the fungus. This includes avoiding direct contact with contaminated soil, wood, and vegetation, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Maintaining good personal hygiene and keeping the skin dry can also help reduce the risk of infection.
See also[edit]

This article is a infectious disease stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian