Platypus
Platypus
The platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus), also known as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. It is one of the few venomous mammals, the male platypus having a spur on the hind foot that delivers a venom capable of causing severe pain to humans.
Taxonomy and etymology[edit]
The platypus is the sole living representative of its family (Ornithorhynchidae) and genus (Ornithorhynchus), though a number of related species have been found in the fossil record. The name "platypus" is derived from the Greek words "platys", which means flat, and "pous", which means foot.
Description[edit]
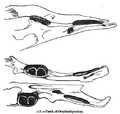
The body and the broad, flat tail of the platypus are covered with dense, brown fur that traps a layer of insulating air to keep the animal warm. The fur is waterproof, and the texture is akin to that of a mole. The platypus uses its tail for storage of fat reserves (an adaptation also found in animals such as the Tasmanian devil).
Distribution and habitat[edit]
The platypus is semiaquatic, inhabiting small streams and rivers over an extensive range from the cold highlands of Tasmania and the Australian Alps to the tropical rainforests of coastal Queensland as far north as the base of the Cape York Peninsula.
Behaviour and ecology[edit]
The platypus is an excellent swimmer and spends much of its time in the water foraging for food. When it is under threat, it will use its venomous spur as a defensive mechanism.
Conservation status[edit]
The platypus is not currently considered to be endangered. However, it is vulnerable to the effects of pollution and it is a protected species throughout its range, with the exception of South Australia.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
| Monotremes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This monotreme-related article is a stub.
|
| Venomous mammals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This venomous mammal related article is a stub.
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian