Pharmacokinetics of estradiol
Pharmacokinetics of Estradiol
Estradiol is a naturally occurring steroid hormone and the primary female sex hormone. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of the menstrual cycle, reproductive system, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females. The pharmacokinetics of estradiol, which refers to how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes the hormone, is a complex process that involves various physiological systems.
Absorption[edit]
Estradiol can be administered in several ways, including orally, transdermally, and via injection. The method of administration significantly impacts the absorption of estradiol. Oral administration results in rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, but it also undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can reduce its bioavailability. Transdermal administration bypasses first-pass metabolism, resulting in higher bioavailability.
Distribution[edit]
Once absorbed, estradiol is distributed throughout the body. It binds to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin in the blood, which transport it to various tissues. Only a small fraction of estradiol remains unbound or "free," and it is this free estradiol that is biologically active.
Metabolism[edit]
Estradiol is primarily metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes. The main metabolic pathway involves conversion to estrone and estriol, both of which are less potent estrogens. Other metabolites include catechol estrogens and methoxyestrogens, which have different biological activities.
Excretion[edit]
Estradiol and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine. Some estradiol is also excreted in the bile and then reabsorbed from the intestine, a process known as enterohepatic circulation.
Factors Affecting Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Several factors can affect the pharmacokinetics of estradiol, including age, body mass, liver function, and concomitant medications. For example, aging and obesity can increase the production of SHBG, which can alter the distribution and metabolism of estradiol. Certain medications, such as rifampicin and phenytoin, can induce cytochrome P450 enzymes and increase the metabolism of estradiol.
See Also[edit]
Pharmacokinetics_of_estradiol[edit]
-
Estradiol
-
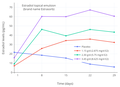
Estradiol levels with a single dose of 2 mg oral estradiol micronized to different particle sizes in women
-
Estradiol levels during therapy with 0.25 mg buccal estradiol in postmenopausal women
-
Estrogen levels after a single 300 μg dose of intranasal estradiol (Aerodiol) in postmenopausal women
-
Estrogen patch
-
Estrogen levels with 1.25 g of 0.06% transdermal estradiol gel (EstroGel) per day in postmenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels with 1.5 or 3.0 mg per day transdermal estradiol gel in postmenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels with 1 mg per day transdermal estradiol gel applied to different amounts of area in postmenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels with estradiol transdermal spray (brand name Lenzetto) in postmenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels with a transdermal estradiol emulsion (brand name Estrasorb) in postmenopausal women
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian