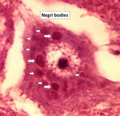
Negri body
Negri bodies are distinct, eosinophilic, cytoplasmic inclusions predominantly found in the neurons of animals and humans infected with the Rabies virus, a member of the Rymoviridae family. First described by and named after Adelchi Negri in 1903, these inclusions are a hallmark of rabies infection and serve as an important diagnostic feature in post-mortem examination.
Characteristics[edit]
Negri bodies vary in size, typically ranging from 0.25 to 27 micrometers in diameter. They are most commonly observed in the Pyramidal cells of the Hippocampus, Purkinje cells of the Cerebellum, and neurons of the Cerebral cortex. Morphologically, Negri bodies appear as round or oval structures with a basophilic core surrounded by a clear halo and an outer eosinophilic ring when stained with Eosin and hematoxylin.
Pathogenesis[edit]
The exact function and composition of Negri bodies are not fully understood, but they are believed to be sites of viral replication and assembly. The presence of Rabies virus nucleoprotein and other viral components within Negri bodies has been confirmed through immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. This suggests that Negri bodies play a crucial role in the rabies virus life cycle, facilitating the accumulation and assembly of viral particles.
Diagnosis[edit]
The detection of Negri bodies in brain tissue is a classical method for diagnosing rabies post-mortem. Techniques such as Direct fluorescent antibody test (dFA) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) have surpassed the use of Negri body identification in terms of sensitivity and specificity. However, in resource-limited settings, the observation of Negri bodies in a brain smear stained with Sellers' stain remains a practical diagnostic approach.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The identification of Negri bodies in the brain tissue of an individual or animal with neurological symptoms suggestive of rabies provides a definitive diagnosis of the disease. Given the fatal nature of rabies once clinical symptoms appear, early detection and confirmation of the virus through the presence of Negri bodies or other diagnostic means are critical for public health measures and the initiation of post-exposure prophylaxis in potential human contacts.
Prevention and Control[edit]
Prevention of rabies is primarily through vaccination of domestic animals, wildlife control, and post-exposure prophylaxis in humans following potential exposure to the virus. Education on avoiding contact with wild animals and the importance of vaccinating pets are also key components of rabies control programs.
See Also[edit]
-
Histopathology of Negri bodies in rabies encephalitis
-
Negri body
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian