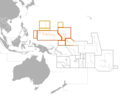
Micronesia
Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a shared cultural history with two other island regions, Polynesia to the east and Melanesia to the south.
Geography[edit]
Micronesia is divided into four main archipelagos, along with numerous outlying islands. The Caroline Islands (which include Palau and the Federated States of Micronesia), the Gilbert Islands (which are part of Kiribati), the Mariana Islands (which include Guam and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands), and the Marshall Islands.
History[edit]
The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521 when Ferdinand Magellan reached the Mariana Islands. Most of Micronesia became part of the Spanish East Indies in the 17th century. In 1898, the islands were sold to Germany and incorporated into German New Guinea.
Culture[edit]
The Micronesian culture was one of the last native cultures of the region to develop. It developed from a mixture of Melanesians, Polynesians, and Filipinos. Because of this mixture of descent, many of the ethnic groups of Micronesia feel closer to some groups in Melanesia, Polynesia or the Philippines.
Economy[edit]
The economy of Micronesia can be described as that of a developing nation with few natural resources, a small population and little industry. The economy is dominated by the service sector, which includes the public sector, trade, and services.
See also[edit]
|
|
|
Micronesia[edit]
-
Oceania UN Geoscheme - Map with Zones
-
Pacific Culture Areas (Philippines + Vanuatu Correction)
-
Mapa Micronesia
-
South Tarawa from the air
-
Suicide Cliff in Saipan
-
Laura beach n tree
-
Castle Bravo Blast
-
Cross spikes club
-
Kili Island - NASA Astronaut Photography
-
Aerial view of Nauru
-
Nauru Denigomodu-Nibok
-
Wake Island by Agate
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian