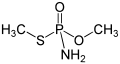
Methamidophos
Methamidophos, also known as O,S-Dimethyl phosphoramidothioate, is an organophosphate insecticide that has been widely used in agriculture to control pests on a variety of crops. Its mode of action involves the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system in insects, leading to their death. However, due to its high toxicity to humans and non-target species, its use has been restricted or banned in many countries.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Methamidophos is a colorless crystalline solid with a slight sulfurous odor. It is soluble in water and most organic solvents, making it highly effective as an agricultural pesticide. The chemical formula for methamidophos is C2H8NO2PS, and its molecular weight is 141.12 g/mol.
Usage[edit]
Historically, methamidophos has been used on a variety of crops, including vegetables, cotton, and potatoes, to control a wide range of insect pests. Its application methods varied from foliar sprays to soil treatments. Despite its effectiveness as an insecticide, the environmental and health risks associated with methamidophos have led to a significant reduction in its use globally.
Health and Environmental Impact[edit]
Methamidophos is highly toxic to humans, animals, and beneficial insects. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, leading to the accumulation of acetylcholine in the nervous system. This accumulation causes continuous nerve signal transmission, resulting in symptoms of poisoning such as headache, dizziness, nausea, and at extreme exposures, respiratory failure, and death.
The environmental impact of methamidophos is also significant. It is highly toxic to aquatic organisms and can contaminate water sources through runoff. Its use has been associated with declines in populations of non-target species, including beneficial insects and birds.
Regulation and Ban[edit]
Due to its high toxicity and environmental impact, the use of methamidophos has been restricted or banned in many countries. Regulatory agencies have established strict guidelines for its use, including permissible exposure limits and recommendations for protective equipment during application. In some regions, its use is completely banned, and alternative pest control methods are encouraged.
Alternatives[edit]
With the increasing restrictions on methamidophos, there has been a shift towards the use of less toxic and more environmentally friendly pest control methods. These include biological control, using natural predators or parasites of pest insects, and the development of new, less toxic chemical insecticides. Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies also play a crucial role in reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
External Links[edit]
![]()
This pesticide-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Methamidophos[edit]
-
Methamidophos.svg
-
Methamidophos-3D-balls-2.png
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian