Ligand-gated ion channel
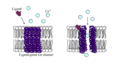
Ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), also known as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (ligand), such as a neurotransmitter. These channels are essential components of the nervous system, playing a key role in the rapid transmission of signals across synapses.
Structure and Function[edit]
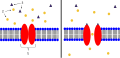
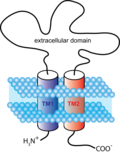
Ligand-gated ion channels are composed of multiple subunits that form a pore through the cell membrane. The structure of these channels allows them to be highly selective for specific ions, such as sodium (Na^+), potassium (K^+), calcium (Ca^2+), or chloride (Cl^-), which move across the membrane when the channel is open. The opening and closing of these channels are directly controlled by the binding of ligands to the extracellular domain of the channel.
The function of LGICs is critical in the nervous system for converting chemical signals into electrical signals, a process known as synaptic transmission. When a neurotransmitter binds to its corresponding ligand-gated ion channel on the postsynaptic cell, it causes a change in the ion permeability of the membrane, leading to a change in the membrane potential. This can result in either excitation or inhibition of the postsynaptic neuron, depending on the type of ion channel and the direction of ion flow.
Types of Ligand-gated Ion Channels[edit]
There are several types of ligand-gated ion channels, classified based on their selective ion permeability and the neurotransmitter that activates them. Major types include:
- Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) - Permeable to Na^+ and K^+, activated by acetylcholine.
- GABA_A receptors - Permeable to Cl^-, activated by gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
- Glycine receptors - Permeable to Cl^-, activated by glycine.
- Glutamate receptors (iGluRs) - Include NMDA, AMPA, and kainate receptors, permeable to Na^+ and K^+, and in some cases Ca^2+, activated by glutamate.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Ligand-gated ion channels are involved in various physiological and pathological processes. Their dysfunction is associated with numerous neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and Alzheimer's disease. Consequently, these channels are important targets for therapeutic drugs. For example, benzodiazepines act on GABA_A receptors to enhance the inhibitory effects of GABA, which is beneficial in treating anxiety and seizures.
Research and Discovery[edit]
The study of ligand-gated ion channels has been a significant area of research in neuroscience and pharmacology. Techniques such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy have been instrumental in elucidating the detailed structure of these channels, providing insights into their function and mechanisms of action. This research has not only advanced our understanding of synaptic transmission but also facilitated the development of drugs targeting these channels.

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This membrane biology related article is a stub.
Ligand-gated_ion_channel[edit]
-
LGIC
-
Ion-Channel Receptor
-
2bg9 opm
-
AMPA receptor
-
Regulation Of AMPAR Trafficking
-
Activated NMDAR
-
Schematic P2XR Subunit V2
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian