Greek language
Greek language is an Indo-European language spoken primarily in Greece, Cyprus, and in various diaspora communities around the world. Greek holds the distinction of having the longest documented history of any living Indo-European language, spanning over 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history; other systems, such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary, were used earlier. The Greek language has contributed significantly to the vocabulary of other languages, particularly in the fields of science, mathematics, philosophy, and theology.
History[edit]
Greek is divided into several historical periods: Mycenaean Greek (16th to 11th century BC), which is recorded in the Linear B script on clay tablets; Ancient Greek, which spans the classical and Hellenistic periods; Medieval Greek or Byzantine Greek, spoken from the Byzantine period up to the fall of Constantinople in 1453; and Modern Greek, which includes the varieties spoken today.
Ancient Greek[edit]
Ancient Greek was a pluricentric language, divided into many dialects. The most important dialects of Classical Greek were Attic Greek, the dialect of Athens, which became the basis for Koine Greek, a common dialect that spread throughout the Alexander's empire and the eastern Mediterranean in the Hellenistic and Roman periods.
Medieval and Modern Greek[edit]
From the Byzantine period onwards, Koine Greek evolved into Medieval Greek, which in turn evolved into Modern Greek. Differences between the two include changes in pronunciation, morphology, syntax, and vocabulary. Modern Greek is divided into two main dialects: Demotic Greek, the vernacular form of the language, and Katharevousa, a more formal version that was used for official and literary purposes until the late 20th century.
Phonology[edit]
The phonological system of Greek has undergone significant changes from its Ancient to its Modern form. The pronunciation of Ancient Greek, particularly vowels and diphthongs, has shifted considerably over the centuries.
Alphabet[edit]
The Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician alphabet, has been used since the 9th century BC. It was the first alphabet to introduce distinct letters for vowels as well as consonants. In its classical and modern forms, the alphabet has 24 letters, beginning with Alpha and ending with Omega.
Grammar[edit]
Greek grammar has also evolved from its ancient to its modern form. The complex inflectional system of Ancient Greek, with its four cases for nouns, three genders, and numerous verb forms, has been simplified in Modern Greek. Modern Greek has three cases for nouns, two genders, and a more streamlined verb conjugation system.
Vocabulary[edit]
Greek vocabulary has been immensely influential in many languages. Many scientific, philosophical, and mathematical terms in English and other Western languages are derived from Greek. Moreover, Greek is still a living language, and its vocabulary continues to evolve.
Dialects[edit]
Modern Greek dialects can be broadly categorized into those of the mainland and the islands. Notable dialects include Cretan Greek, Pontic Greek, and Cypriot Greek. Despite the diversity, Standard Modern Greek, based on Demotic, is taught in schools and used in official communications.
Influence on Other Languages[edit]
Greek has had a profound impact on the languages of the world, especially in the realms of science, philosophy, and the arts. The Greek alphabet also served as a basis for the Cyrillic alphabet and the Latin alphabet.
Conclusion[edit]
The Greek language, with its rich history, extensive literature, and significant impact on other languages, remains a vital and dynamic component of world heritage. Its evolution from Mycenaean Greek to the modern language spoken today is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
Greek_language[edit]
-
Homer British Museum
-
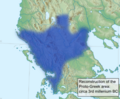
Proto Greek Area reconstruction
-
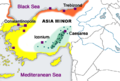
Anatolian Greek dialects
-
Modern Greek dialects
-
Greek language in the Russian Empire (1897)
-
Cypriot syllabic inscription 600-500BC
-
Greek alphabet variants
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian