Gliomatosis cerebri

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Gliomatosis cerebri | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, seizures, cognitive dysfunction, personality changes |
| Complications | Increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Progressive |
| Types | Type 1 (diffuse), Type 2 (focal) |
| Causes | Unknown, possibly genetic mutations |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, radiation exposure |
| Diagnosis | MRI, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, palliative care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor, median survival 12-24 months |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare type of brain tumor
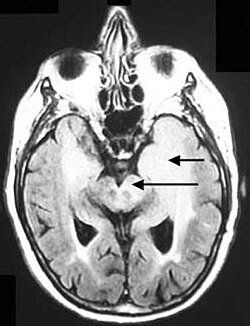
Gliomatosis cerebri is a rare and aggressive form of brain tumor characterized by the diffuse infiltration of glial cells across multiple regions of the central nervous system. Unlike other types of glioma, gliomatosis cerebri does not form a distinct mass but rather spreads extensively, often involving at least three cerebral lobes.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Gliomatosis cerebri is primarily composed of astrocytes, a type of glial cell, and is classified as a World Health Organization (WHO) grade III tumor. The diffuse nature of the tumor makes it challenging to diagnose and treat. The tumor cells infiltrate the white matter and gray matter, disrupting normal neural pathways and leading to a variety of neurological symptoms.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of gliomatosis cerebri are varied and depend on the regions of the brain affected. Common symptoms include:
Diagnosis[edit]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the primary tool for diagnosing gliomatosis cerebri. The MRI typically shows diffuse hyperintensity on T2-weighted images, with extensive involvement of the brain parenchyma. Biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to differentiate it from other types of diffuse gliomas.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for gliomatosis cerebri are limited due to its diffuse nature. Standard treatment approaches include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy with agents such as temozolomide
- Corticosteroids to reduce cerebral edema
Surgical resection is generally not feasible due to the widespread infiltration of the tumor.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with gliomatosis cerebri is generally poor, with a median survival of approximately 12 to 24 months after diagnosis. The aggressive nature of the tumor and its resistance to conventional therapies contribute to the poor outcome.
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian