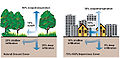
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is a term used to describe the process by which water is transferred from the land to the atmosphere by evaporation from the soil and other surfaces and by transpiration from plants. It is a critical component of the hydrological cycle, which describes the movement of water within the Earth's atmosphere, surface, and subsurface environments. Understanding evapotranspiration is essential for various fields, including hydrology, agriculture, meteorology, and environmental science, as it plays a significant role in water resource management, climate modeling, and agricultural planning.
Overview[edit]
Evapotranspiration combines two processes: evaporation and transpiration. Evaporation is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a vapor state, occurring from surfaces such as soil, water bodies, and wet vegetation. Transpiration, on the other hand, is the process by which water within plants is transferred to the atmosphere as water vapor through small openings in leaves called stomata. Together, these processes contribute to the amount of moisture released into the atmosphere, influencing local and global climate patterns.
Factors Influencing Evapotranspiration[edit]
Several factors can affect the rate of evapotranspiration, including:
- Climate: Temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation are critical climatic factors that influence evapotranspiration rates.
- Soil Type: The characteristics of the soil, such as texture, structure, and moisture content, can impact the rate of evaporation from the soil surface.
- Vegetation Type: Different types of vegetation transpire at different rates due to variations in leaf area, root depth, and plant physiology.
- Water Availability: The availability of water in the soil for uptake by plants can limit transpiration rates.
Measurement and Estimation[edit]
Measuring evapotranspiration directly is challenging and often involves complex instruments and methodologies. However, several methods have been developed to estimate evapotranspiration rates, including:
- Lysimeters: Devices that measure the amount of water used by plants growing within them.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite or aerial imagery can be used to estimate evapotranspiration over large areas.
- Empirical Models: Mathematical models that estimate evapotranspiration based on climatic and environmental data.
Importance in Water Resource Management[edit]
Evapotranspiration plays a crucial role in water resource management. It is a significant component of the water balance equation, which is used to manage water resources in agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation. Understanding evapotranspiration rates helps in the efficient allocation of water for irrigation, the design of water conservation strategies, and the prediction of water availability in reservoirs and aquifers.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit]
One of the main challenges in the study of evapotranspiration is the accurate measurement and estimation of its rates across different spatial and temporal scales. Advances in technology, such as improved remote sensing techniques and more sophisticated models, are expected to enhance our understanding and prediction of evapotranspiration patterns. Additionally, climate change poses a challenge to predicting future evapotranspiration rates, as changing temperature and precipitation patterns may alter water cycles in unpredictable ways.
See Also[edit]
-
Diagram illustrating the surface water cycle
-
Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) diagram
-
Natural and impervious cover diagrams by EPA
-
Design of a lysimeter for measuring evapotranspiration
-
Classification of remote sensing-based ET models
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian