Elastography
Medical imaging technique to map tissue stiffness
Elastography is a medical imaging modality that maps the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue. It is used to detect and characterize various diseases, particularly those that alter the mechanical properties of tissues, such as cancer and fibrosis.
Principles of Elastography[edit]
Elastography is based on the principle that pathological changes in tissue often result in changes in its mechanical properties. For instance, cancerous tissues are generally stiffer than normal tissues. Elastography techniques measure the response of tissue to an applied force, which can be mechanical, acoustic, or electromagnetic, and then calculate the tissue's stiffness or elasticity.
Techniques of Elastography[edit]
There are several techniques used in elastography, each with its own advantages and applications:
Ultrasound Elastography[edit]
Ultrasound elastography uses sound waves to measure tissue stiffness. It includes methods such as:
- Strain Elastography: This technique involves applying a mechanical compression to the tissue and measuring the resulting strain. It is often used in breast and thyroid imaging.
- Shear Wave Elastography: This method generates shear waves within the tissue using focused ultrasound beams. The speed of these waves is measured to determine tissue stiffness. It is commonly used in liver and musculoskeletal imaging.

Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)[edit]
Magnetic resonance elastography uses MRI to visualize the propagation of mechanical waves through tissues. It is particularly useful for imaging the liver and brain.
Transient Elastography[edit]
Transient elastography is a non-invasive method that uses a mechanical impulse to generate shear waves in the liver. It is widely used for assessing liver fibrosis.
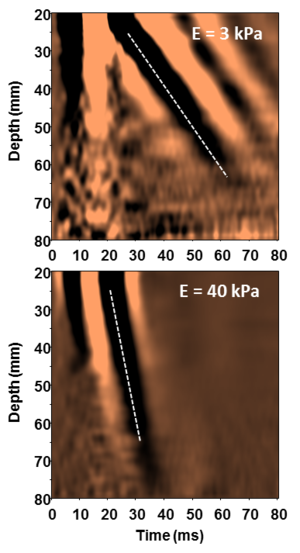
Applications of Elastography[edit]
Elastography is used in various clinical applications, including:
Breast Imaging[edit]
Elastography is used to differentiate between benign and malignant breast lesions. Malignant tumors tend to be stiffer than benign ones.

Liver Fibrosis Assessment[edit]
Elastography is a key tool in assessing liver fibrosis, providing a non-invasive alternative to liver biopsy.
Thyroid Nodule Evaluation[edit]
Elastography helps in evaluating thyroid nodules, distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules based on stiffness.

Musculoskeletal Imaging[edit]
Elastography is used to assess muscle stiffness and detect abnormalities in musculoskeletal tissues.

Advantages and Limitations[edit]
Elastography offers several advantages, including being non-invasive, providing quantitative data, and enhancing the diagnostic accuracy of conventional imaging techniques. However, it also has limitations, such as operator dependency and variability in results due to different equipment and techniques.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian