Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
A pharmaceutical agent or drug that is categorized by its ability to alter the progression of an autoimmune disease as opposed to just treating the inflammation or symptoms.
Etiology[edit]
The term disease modifying antirheumatic drug was applied in order to differentiate those drugs that have the potential to slow the progression of the rheumatoid arthritis such as methotrexate, from the symptomatic treatment with NSAIDs that just treat inflammation and steroids that reduce inflammation but do not slow or stop the progression of the disease.
Other diseases[edit]
Overtime, the DMRD's is also used in other conditions such as Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, myasthenia gravis, sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis etc.
Types[edit]
- certolizumab pegol
- chloroquine (anti-malarial)
- ciclosporin (Cyclosporin A)
- D-penicillamine (seldom used today)
- gold salts (sodium aurothiomalate, auranofin) (seldom used today)
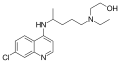
- [[hydroxychloroquine (anti-malarial)
- methotrexate (MTX)
- sulfasalazine (SSZ)
Types of DMRD's[edit]
DMRD's can be classified as biologics such as infliximab, ethanercept, abatacept, adalimumab, anakinra, apremilast etc. and synthetic or traditional DMRD's such as methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, gold salts
| DMARDs, their mechanisms of action, JIA approval status, and samples of significant warnings from the drug product labels. | ' | ' | ' | ' |
| Generic Name | US Trade Name | Mechanism of Action | Approved by FDA for JIA | Warnings – Increased Risk |
| Abatacept | Orencia | anti-CD28, T-cell costimulator antibodies | Yes | infections |
| biologic | ||||
| Adalimumab | Humira | TNF inhibitor | Yes | infections |
| biologic | cancer | |||
| Anakinra | Kineret | IL-1 receptor antagonist | No | infections |
| biologic | ||||
| Canakinumab | Ilaris | IL-1 blocker | No | vertigo |
| biologic | ||||
| Etanercept | Enbrel | TNF inhibitor | Yes | infections |
| biologic | cancer | |||
| Infliximab | Remicade | TNF inhibitor | No | infections |
| biologic | cancer | |||
| IVIG | Baygam | interaction with activating Fc receptors | No | hepatitis |
| Carimune NF | biologic | acute renal failure | ||
| Flebogamma 5% | venous thrombosis | |||
| DIF | aseptic meningitis | |||
| Gammar P | ||||
| Gamunex 10% | ||||
| Gammagard S/D | ||||
| Gammagard Liquid 10% | ||||
| Gammar P | ||||
| Iveegam EN | ||||
| Octagam 5% | ||||
| Panglobulin | ||||
| Polygam S/D | ||||
| Privigen 10% | ||||
| Vivaglobin | ||||
| Rilonacept | Arcalyst | IL-1 blocker | No | infection |
| biologic | ||||
| Rituximab | Rituxan | binds to CD20 antigen | No | progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
| biologic | severe skin reactions | |||
| infusion reactions | ||||
| Tocilizumab | Actemra | IL-6 receptor antagonist | No | infections |
| biologic | elevated lipid levels | |||
| Azathioprine | Azasan | purine synthesis inhibitor | No | cancer |
| Imuran | nonbiologic | bone marrow suppression | ||
| Cyclosporine A | Neoral | inhibits calcineurin | No | infections |
| Gengraf | nonbiologic | nephrotoxicity hepatotoxicity | ||
| D-Penicillamine | Depen | unknown (may lower IgM rheumatoid factor; depresses T-cell activity) | No | allergic reactions |
| Cuprimine | nonbiologic | Goodpasture’s syndrome | ||
| hematologic toxicities | ||||
| hepatotoxicity | ||||
| myasthenia gravis | ||||
| Hydroxy-chloroquine | Plaquenil | not well understood (may reduce T-lymphocyte transformation and chemotaxis) | No | kidney damage |
| nonbiologic | retinopathy | |||
| Leflunomide | Arava | isoxazole immunomodulatory agent | No | hepatotoxicity |
| nonbiologic | ||||
| Methotrexate | Methotrexate LPF | unknown (antimetabolite; inhibits dihydrofolic acid reductase) | Yes | hepatotoxicity |
| nonbiologic | cancer | |||
| Mycophenolate mofetil | CellCept | guanosine synthesis inhibitor | No | cancer |
| nonbiologic | bone marrow suppression | |||
| Sulfasalazine | Azulfidine sulfazine | unknown | Yes | bone marrow suppression |
| nonbiologic | hepatotoxicity | |||
| Stevens Johnson syndrome | ||||
| Tacrolimus (FK506) | Prograf | reduces T-cell and IL-2 activity | No | cancer |
| nonbiologic | infection | |||
| Thalidomide | Thalomid | unknown | No | birth defects |
| nonbiologic | neuropathy | |||
| Major chemical drug groups | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Specific antirheumatic products / DMARDs (M01C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian