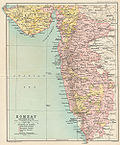
Bombay Presidency
Bombay Presidency[edit]
The Bombay Presidency, also known as the Bombay Province, was a former administrative division of British India. It was one of the three Presidencies of British India, the others being the Bengal Presidency and the Madras Presidency. The Bombay Presidency was established in the 17th century and existed until the mid-20th century, playing a significant role in the colonial administration of India.
History[edit]
The origins of the Bombay Presidency can be traced back to the early 17th century when the British East India Company established a trading post in the area. In 1661, the islands of Bombay were given to the British as part of the dowry of Catherine of Braganza when she married Charles II of England. The British East India Company took control of the islands in 1668, and Bombay became an important trading center.
In 1687, the Company moved its headquarters from Surat to Bombay, and the city began to grow rapidly. By the early 19th century, the Bombay Presidency had expanded to include large parts of western India, including the present-day states of Maharashtra, Gujarat, and parts of Karnataka.
Administration[edit]
The Bombay Presidency was governed by a Governor, who was appointed by the British Crown. The Governor was assisted by a council, and the administration was divided into several districts, each headed by a Collector. The Presidency had its own army, known as the Bombay Army, which was part of the British Indian Army.
The capital of the Presidency was Bombay, which was also the largest city and the main port. The city became a major center for trade, commerce, and industry, and played a crucial role in the economic development of the region.
Economy[edit]
The economy of the Bombay Presidency was primarily based on agriculture, with cotton being the main cash crop. The region also had significant textile and manufacturing industries, particularly in Bombay. The development of the railway network in the 19th century further boosted trade and commerce in the Presidency.
The Presidency was also known for its rich natural resources, including coal, iron ore, and manganese. These resources were exploited by the British for industrial purposes, contributing to the economic growth of the region.
Education and Society[edit]
The Bombay Presidency was a center of education and social reform during the British period. The University of Bombay was established in 1857, and it became one of the leading educational institutions in India. The Presidency was also home to several prominent social reformers, such as Jyotirao Phule and B. R. Ambedkar, who worked towards the upliftment of marginalized communities.
Legacy[edit]
The Bombay Presidency played a significant role in the history of British India, and its legacy can still be seen in the modern states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. The city of Bombay, now known as Mumbai, remains one of the largest and most important cities in India.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Peter,
A History of India, Palgrave Macmillan, 2002, ISBN 978-0-333-69129-8,
- John,
India: A History, HarperCollins, 2000, ISBN 978-0-00-255717-7,
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
-
Bombay Presidency
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian