Bias



Bias refers to a tendency or inclination that affects judgment or decision-making in a way that is considered to be unfair, prejudiced, or favoring one side over another. Bias can manifest in various contexts, including but not limited to social bias, cognitive bias, statistical bias, and media bias. It can arise from conscious or unconscious beliefs or attitudes and can have significant impacts on individual behavior, societal norms, and decision-making processes in fields such as law, science, education, and politics.
Types of Bias[edit]
Bias can be categorized into several types, each affecting perception, decision-making, and judgment in different ways.
Cognitive Bias[edit]
Cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, whereby inferences about other people and situations may be drawn in an illogical fashion. Cognitive biases are often a result of the brain's attempt to simplify information processing. They are divided into various categories, such as confirmation bias, where individuals favor information that confirms their preconceptions, and anchoring bias, where an individual relies too heavily on an initial piece of information to make subsequent judgments.
Social Bias[edit]
Social bias includes biases that occur in social settings, where personal judgments are influenced by social factors and stereotypes. Examples include racism, sexism, and ageism, where judgments about individuals are based on their race, gender, or age, respectively, rather than their individual merits.
Statistical Bias[edit]
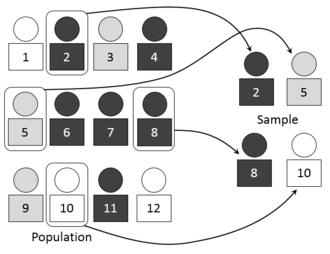
Statistical bias refers to a systematic error that causes certain estimates to deviate from the true values in a particular direction. It can occur in the collection, analysis, interpretation, and review of data. An example of statistical bias is selection bias, where the sample obtained is not representative of the population intended to be analyzed.
Media Bias[edit]
Media bias involves the bias of journalists and news producers within the mass media, in the selection of events and stories that are reported, and how they are covered. This can manifest in the portrayal of news in a manner that conflicts with standards of professional journalism, such as presenting news in a partial or prejudiced manner.
Causes of Bias[edit]
The causes of bias are multifaceted and can include personal experiences, societal influences, cognitive mechanisms, and information processing shortcuts (heuristics). Education and awareness can help mitigate some forms of bias, but others may be more deeply ingrained and require more concerted efforts to address.
Effects of Bias[edit]
The effects of bias can be widespread, affecting societal equality, justice, and the integrity of scientific research. In the legal system, for example, bias can lead to unfair judgments and sentencing. In the workplace, bias can result in unequal opportunities and treatment. In science, bias can skew research findings and conclusions.
Combating Bias[edit]
Efforts to combat bias involve both individual and collective actions. Education and training programs, such as diversity and inclusion training, can help individuals recognize and address their biases. Institutional policies and practices, such as blind audition processes in orchestras or anonymized resume reviews in hiring, can help reduce the impact of bias in decision-making.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


