Artificial bone
Artificial Bone[edit]

Artificial bone is a synthetic material designed to mimic the properties of natural bone. It is used in medical applications to replace or repair damaged bone tissue. The development of artificial bone is a significant advancement in the field of orthopedics and biomaterials.
Composition and Structure[edit]
Artificial bone materials are typically composed of biocompatible substances that can integrate with natural bone tissue. Common materials used include hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, and various polymers. These materials are chosen for their ability to support bone growth and their structural similarity to natural bone.
Hydroxyapatite[edit]
Hydroxyapatite is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite. It is the main inorganic component of natural bone and teeth, making it an ideal candidate for artificial bone applications. Hydroxyapatite is known for its excellent biocompatibility and osteoconductivity, which means it supports the growth of new bone cells.
Polymers[edit]
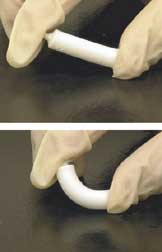
Polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyglycolic acid (PGA) are often used in combination with ceramic materials to create composite scaffolds. These polymers are biodegradable and can be engineered to degrade at a rate that matches the growth of new bone tissue.
Fabrication Techniques[edit]
The fabrication of artificial bone involves advanced techniques to ensure the material mimics the complex structure of natural bone. These techniques include solid freeform fabrication, electrospinning, and 3D printing.
Solid Freeform Fabrication[edit]

Solid freeform fabrication (SFF) is a technique used to create complex structures layer by layer. This method allows for precise control over the architecture of the scaffold, which is crucial for ensuring the mechanical properties and porosity of the artificial bone match those of natural bone.
Biological Integration[edit]
For artificial bone to be successful, it must integrate with the host tissue. This involves the processes of osteoconduction, osteoinduction, and osseointegration.
Osteoconduction[edit]
Osteoconduction refers to the ability of the scaffold to support the growth of new bone along its surface. This is facilitated by the porous structure of the scaffold, which allows for the infiltration of bone-forming cells and nutrients.
Osteoinduction[edit]
Osteoinduction is the process by which the scaffold induces the differentiation of progenitor cells into osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation. This can be enhanced by incorporating growth factors into the scaffold.
Osseointegration[edit]
Osseointegration is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of the artificial implant. This is essential for the long-term stability of the implant.
Applications[edit]
Artificial bone is used in a variety of medical applications, including bone grafting, dental implants, and joint replacement. It is particularly useful in cases where natural bone is unable to heal on its own, such as in large bone defects or in patients with compromised healing abilities.
Future Directions[edit]
Research in artificial bone is ongoing, with a focus on improving the materials and techniques used to create these implants. Advances in nanotechnology and tissue engineering hold promise for the development of more effective and versatile artificial bone materials.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian