Marginal zone lymphoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Marginal zone lymphoma | |||
| image = [[File:Marginal_zone_lymphoma_-_kidney_--_high_mag.jpg|250px]] | |||
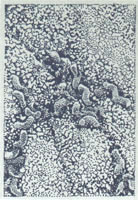
| caption = Micrograph of marginal zone lymphoma involving the kidney. H&E stain. | |||
| field = [[Hematology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Lymphadenopathy]], [[fatigue]], [[fever]], [[night sweats]], [[weight loss]] | |||
| complications = Transformation to [[diffuse large B-cell lymphoma]] | |||
| onset = Typically in adults | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = [[Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma]], [[Nodal marginal zone lymphoma]], [[Splenic marginal zone lymphoma]] | |||
| causes = Unknown, but associated with [[chronic inflammation]] and [[autoimmune diseases]] | |||
| risks = [[Helicobacter pylori]] infection, [[Hepatitis C]] infection, [[autoimmune disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Biopsy]], [[immunophenotyping]], [[cytogenetic analysis]] | |||
| differential = [[Follicular lymphoma]], [[chronic lymphocytic leukemia]], [[mantle cell lymphoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]], [[immunotherapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good, but varies with type and stage | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Dark,_light,_mantle_and_marginal_zones_of_a_secondary_follicle.png|Dark, light, mantle, and marginal zones of a secondary follicle|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Helicobacter_pylori2.jpg|Helicobacter pylori|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Bcr_B-cell_receptor.jpg|B-cell receptor (BCR)|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Marginal zone lymphoma''' ('''MZL''') is a type of [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] that affects [[B cells]]. It is named for the marginal zone of the [[lymph node]] where these cells are found. MZL is a slow-growing, or indolent, lymphoma. There are three types of MZL: extranodal MZL of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), nodal MZL, and splenic MZL. | '''Marginal zone lymphoma''' ('''MZL''') is a type of [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] that affects [[B cells]]. It is named for the marginal zone of the [[lymph node]] where these cells are found. MZL is a slow-growing, or indolent, lymphoma. There are three types of MZL: extranodal MZL of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), nodal MZL, and splenic MZL. | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
===Extranodal MZL of MALT=== | ===Extranodal MZL of MALT=== | ||
[[Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma]] or MALT lymphoma, is the most common type of MZL. It can occur in various parts of the body, including the stomach, lungs, eyes, and skin. | [[Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma]] or MALT lymphoma, is the most common type of MZL. It can occur in various parts of the body, including the stomach, lungs, eyes, and skin. | ||
===Nodal MZL=== | ===Nodal MZL=== | ||
[[Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma]] is a rare type of MZL that occurs in the lymph nodes. | [[Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma]] is a rare type of MZL that occurs in the lymph nodes. | ||
===Splenic MZL=== | ===Splenic MZL=== | ||
[[Splenic marginal zone lymphoma]] affects the spleen and the blood. It can also affect the bone marrow. | [[Splenic marginal zone lymphoma]] affects the spleen and the blood. It can also affect the bone marrow. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of MZL can vary depending on the type and location of the lymphoma. They may include swelling of the lymph nodes, stomach pain, fatigue, and weight loss. | Symptoms of MZL can vary depending on the type and location of the lymphoma. They may include swelling of the lymph nodes, stomach pain, fatigue, and weight loss. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of MZL typically involves a [[biopsy]] of the affected tissue. Other tests may include blood tests, imaging tests, and a bone marrow biopsy. | Diagnosis of MZL typically involves a [[biopsy]] of the affected tissue. Other tests may include blood tests, imaging tests, and a bone marrow biopsy. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for MZL depends on the type and stage of the lymphoma, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include [[watchful waiting]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]], [[immunotherapy]], and in some cases, [[surgery]]. | Treatment for MZL depends on the type and stage of the lymphoma, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include [[watchful waiting]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]], [[immunotherapy]], and in some cases, [[surgery]]. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for MZL is generally good, with many patients living for many years after diagnosis. However, the disease is often not curable and may require ongoing treatment. | The prognosis for MZL is generally good, with many patients living for many years after diagnosis. However, the disease is often not curable and may require ongoing treatment. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Lymphoma]] | * [[Lymphoma]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 42: | ||
* [[B cells]] | * [[B cells]] | ||
* [[Lymph node]] | * [[Lymph node]] | ||
[[Category:Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] | [[Category:Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] | ||
[[Category:Lymphoma]] | [[Category:Lymphoma]] | ||
[[Category:Types of cancer]] | [[Category:Types of cancer]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:22, 12 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Marginal zone lymphoma | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lymphadenopathy, fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss |
| Complications | Transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| Onset | Typically in adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma, Nodal marginal zone lymphoma, Splenic marginal zone lymphoma |
| Causes | Unknown, but associated with chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases |
| Risks | Helicobacter pylori infection, Hepatitis C infection, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, immunophenotyping, cytogenetic analysis |
| Differential diagnosis | Follicular lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, mantle cell lymphoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good, but varies with type and stage |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |


Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) is a type of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects B cells. It is named for the marginal zone of the lymph node where these cells are found. MZL is a slow-growing, or indolent, lymphoma. There are three types of MZL: extranodal MZL of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), nodal MZL, and splenic MZL.
Types[edit]
Extranodal MZL of MALT[edit]
Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma or MALT lymphoma, is the most common type of MZL. It can occur in various parts of the body, including the stomach, lungs, eyes, and skin.
Nodal MZL[edit]
Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma is a rare type of MZL that occurs in the lymph nodes.
Splenic MZL[edit]
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma affects the spleen and the blood. It can also affect the bone marrow.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of MZL can vary depending on the type and location of the lymphoma. They may include swelling of the lymph nodes, stomach pain, fatigue, and weight loss.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of MZL typically involves a biopsy of the affected tissue. Other tests may include blood tests, imaging tests, and a bone marrow biopsy.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for MZL depends on the type and stage of the lymphoma, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include watchful waiting, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and in some cases, surgery.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for MZL is generally good, with many patients living for many years after diagnosis. However, the disease is often not curable and may require ongoing treatment.


