Retinopathy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Retinopathy | |||
| image = [[File:Fundus_retinopathy_EDA03.JPG|250px]] | |||
| caption = Fundus photograph showing signs of retinopathy | |||
| field = [[Ophthalmology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Vision loss]], [[blurred vision]], [[floaters (eye)|floaters]], [[difficulty seeing at night]] | |||
| complications = [[Blindness]], [[macular edema]], [[retinal detachment]] | |||
| onset = Varies depending on type | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = [[Diabetic retinopathy]], [[hypertensive retinopathy]], [[retinopathy of prematurity]] | |||
| causes = [[Diabetes mellitus]], [[hypertension]], [[premature birth]] | |||
| risks = Poor control of blood sugar, high blood pressure, premature birth | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ophthalmoscopy]], [[fluorescein angiography]], [[optical coherence tomography]] | |||
| differential = [[Macular degeneration]], [[retinal vein occlusion]], [[vitreous hemorrhage]] | |||
| prevention = Control of blood sugar and blood pressure, regular eye exams | |||
| treatment = [[Laser photocoagulation]], [[anti-VEGF therapy]], [[vitrectomy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; early detection and treatment can prevent vision loss | |||
| frequency = Common in individuals with diabetes or hypertension | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Fundus Proliferative retinopathy EDA01.JPG|Proliferative Retinopathy|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Retinopathy''' is a disease of the [[retina]], which is the thin, light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It can occur as a result of various conditions, most commonly [[diabetes]] and [[high blood pressure]]. Retinopathy can lead to [[vision loss]] and is a leading cause of [[blindness]] among working-age adults. | '''Retinopathy''' is a disease of the [[retina]], which is the thin, light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It can occur as a result of various conditions, most commonly [[diabetes]] and [[high blood pressure]]. Retinopathy can lead to [[vision loss]] and is a leading cause of [[blindness]] among working-age adults. | ||
==Types of Retinopathy== | ==Types of Retinopathy== | ||
There are several types of retinopathy, including: | There are several types of retinopathy, including: | ||
* '''[[Diabetic retinopathy]]''': This is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. It is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and the leading cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults. | * '''[[Diabetic retinopathy]]''': This is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. It is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and the leading cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults. | ||
* '''[[Hypertensive retinopathy]]''': This is damage to the retina and its blood vessels due to high blood pressure. It can lead to bleeding in the eye, blurred vision and complete loss of vision. | * '''[[Hypertensive retinopathy]]''': This is damage to the retina and its blood vessels due to high blood pressure. It can lead to bleeding in the eye, blurred vision and complete loss of vision. | ||
* '''[[Retinopathy of prematurity]]''': This is a potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants weighing about 2¾ pounds (1250 grams) or less that are born before 31 weeks of gestation. | |||
* '''[[Retinopathy of prematurity]]''': This is a potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants weighing about | |||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of retinopathy can include: | Symptoms of retinopathy can include: | ||
* [[Blurred vision]] | * [[Blurred vision]] | ||
* [[Floaters]] | * [[Floaters]] | ||
* [[Vision loss]] | * [[Vision loss]] | ||
* [[Difficulty seeing at night]] | * [[Difficulty seeing at night]] | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Retinopathy can be diagnosed through a comprehensive [[eye examination]]. This can include: | Retinopathy can be diagnosed through a comprehensive [[eye examination]]. This can include: | ||
* '''Visual acuity test''': This uses an eye chart to measure how well a person sees at various distances. | * '''Visual acuity test''': This uses an eye chart to measure how well a person sees at various distances. | ||
* '''Dilated eye exam''': Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils. This allows the eye care professional to see more of the retina and look for signs of disease. | * '''Dilated eye exam''': Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils. This allows the eye care professional to see more of the retina and look for signs of disease. | ||
* '''Tonometry''': This is a test that measures the pressure inside the eye. | * '''Tonometry''': This is a test that measures the pressure inside the eye. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for retinopathy depends on the underlying cause. For example, good control of diabetes and high blood pressure can slow the progression of retinopathy. In some cases, laser treatment or surgery may be needed to seal leaking blood vessels or to remove blood from the eye. | Treatment for retinopathy depends on the underlying cause. For example, good control of diabetes and high blood pressure can slow the progression of retinopathy. In some cases, laser treatment or surgery may be needed to seal leaking blood vessels or to remove blood from the eye. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Eye disease]] | * [[Eye disease]] | ||
* [[Vision loss]] | * [[Vision loss]] | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
[[Category:Eye diseases]] | [[Category:Eye diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Diabetes]] | [[Category:Diabetes]] | ||
[[Category:High blood pressure]] | [[Category:High blood pressure]] | ||
[[Category:Vision loss]] | [[Category:Vision loss]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:42, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Retinopathy | |
|---|---|
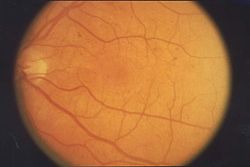
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Vision loss, blurred vision, floaters, difficulty seeing at night |
| Complications | Blindness, macular edema, retinal detachment |
| Onset | Varies depending on type |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Diabetic retinopathy, hypertensive retinopathy, retinopathy of prematurity |
| Causes | Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, premature birth |
| Risks | Poor control of blood sugar, high blood pressure, premature birth |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmoscopy, fluorescein angiography, optical coherence tomography |
| Differential diagnosis | Macular degeneration, retinal vein occlusion, vitreous hemorrhage |
| Prevention | Control of blood sugar and blood pressure, regular eye exams |
| Treatment | Laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF therapy, vitrectomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; early detection and treatment can prevent vision loss |
| Frequency | Common in individuals with diabetes or hypertension |
| Deaths | N/A |

Retinopathy is a disease of the retina, which is the thin, light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It can occur as a result of various conditions, most commonly diabetes and high blood pressure. Retinopathy can lead to vision loss and is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults.
Types of Retinopathy[edit]
There are several types of retinopathy, including:
- Diabetic retinopathy: This is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. It is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and the leading cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults.
- Hypertensive retinopathy: This is damage to the retina and its blood vessels due to high blood pressure. It can lead to bleeding in the eye, blurred vision and complete loss of vision.
- Retinopathy of prematurity: This is a potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants weighing about 2¾ pounds (1250 grams) or less that are born before 31 weeks of gestation.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of retinopathy can include:
Diagnosis[edit]
Retinopathy can be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination. This can include:
- Visual acuity test: This uses an eye chart to measure how well a person sees at various distances.
- Dilated eye exam: Drops are placed in the eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils. This allows the eye care professional to see more of the retina and look for signs of disease.
- Tonometry: This is a test that measures the pressure inside the eye.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for retinopathy depends on the underlying cause. For example, good control of diabetes and high blood pressure can slow the progression of retinopathy. In some cases, laser treatment or surgery may be needed to seal leaking blood vessels or to remove blood from the eye.


