Hyperparathyroidism: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hyperparathyroidism | |||
| image = [[File:Illu_thyroid_parathyroid.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Illustration of the thyroid and parathyroid glands | |||
| field = [[Endocrinology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Fatigue (medical)|Fatigue]], [[depression (mood)|depression]], [[bone pain]], [[kidney stones]], [[osteoporosis]] | |||
| complications = [[Osteoporosis]], [[kidney stones]], [[cardiovascular disease]] | |||
| onset = Typically [[middle age]] | |||
| duration = Long-term | |||
| causes = Overactivity of one or more of the [[parathyroid glands]] | |||
| risks = [[Radiation therapy]], [[genetic disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Blood test]]s showing elevated [[calcium]] and [[parathyroid hormone]] levels | |||
| differential = [[Hypercalcemia]], [[malignancy]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[medication]] | |||
| medication = [[Bisphosphonates]], [[calcimimetics]] | |||
| frequency = 1-7 per 1,000 people | |||
}} | |||
[[Hyperparathyroidism]] is a condition characterized by an overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands. This excess PTH can lead to high levels of calcium in the blood, which can cause a variety of health problems. | [[Hyperparathyroidism]] is a condition characterized by an overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands. This excess PTH can lead to high levels of calcium in the blood, which can cause a variety of health problems. | ||
[[File:3D Medical Animation still shot Hyperparathyroidism.jpg|thumb|3D Medical Animation still shot Hyperparathyroidism]] | [[File:3D Medical Animation still shot Hyperparathyroidism.jpg|left|thumb|3D Medical Animation still shot Hyperparathyroidism]] | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
* There are two main types of hyperparathyroidism: primary and secondary. | * There are two main types of hyperparathyroidism: primary and secondary. | ||
* [[Primary hyperparathyroidism]] is caused by an enlargement or adenoma in one or more of the parathyroid glands. This leads to an overproduction of PTH and subsequent high calcium levels in the blood. | * [[Primary hyperparathyroidism]] is caused by an enlargement or adenoma in one or more of the parathyroid glands. This leads to an overproduction of PTH and subsequent high calcium levels in the blood. | ||
* [[Secondary hyperparathyroidism]] is a response to low calcium levels in the blood. This can be due to various reasons such as vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, or dietary insufficiency. The low calcium levels stimulate the parathyroid glands to produce more PTH. | * [[Secondary hyperparathyroidism]] is a response to low calcium levels in the blood. This can be due to various reasons such as vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, or dietary insufficiency. The low calcium levels stimulate the parathyroid glands to produce more PTH. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
* Hyperparathyroidism can often be asymptomatic, especially in its early stages. When symptoms do occur, they may include: | * Hyperparathyroidism can often be asymptomatic, especially in its early stages. When symptoms do occur, they may include: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 31: | ||
* Kidney stones | * Kidney stones | ||
* Nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite | * Nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Hyperparathyroidism is often diagnosed through blood tests that show high levels of PTH and calcium. Other tests, like bone density scans and kidney function tests, may also be used. In some cases, imaging tests can help identify an enlarged parathyroid gland. | Hyperparathyroidism is often diagnosed through blood tests that show high levels of PTH and calcium. Other tests, like bone density scans and kidney function tests, may also be used. In some cases, imaging tests can help identify an enlarged parathyroid gland. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In primary hyperparathyroidism, surgery to remove the affected parathyroid gland(s) may be necessary. For secondary hyperparathyroidism, treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause, such as increasing calcium or vitamin D intake or managing kidney disease. | Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In primary hyperparathyroidism, surgery to remove the affected parathyroid gland(s) may be necessary. For secondary hyperparathyroidism, treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause, such as increasing calcium or vitamin D intake or managing kidney disease. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Parathyroid gland]] | * [[Parathyroid gland]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 40: | ||
* [[Calcium]] | * [[Calcium]] | ||
* [[Vitamin D]] | * [[Vitamin D]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* Khan, Aliya (2017). "Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Diagnosis, Differential Diagnosis, and Evaluation". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. | * Khan, Aliya (2017). "Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Diagnosis, Differential Diagnosis, and Evaluation". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. | ||
* Komaba, Hirotaka; Fukagawa, Masafumi (2012). "Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathogenesis and Treatment". Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis. | * Komaba, Hirotaka; Fukagawa, Masafumi (2012). "Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathogenesis and Treatment". Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis. | ||
* Bilezikian, John P.; Khan, Aliya A.; Potts, John T. (2009). "Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: Summary statement from the Fourth International Workshop". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. | * Bilezikian, John P.; Khan, Aliya A.; Potts, John T. (2009). "Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: Summary statement from the Fourth International Workshop". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
[[Hyperparathyroidism - MedlinePlus]] | [[Hyperparathyroidism - MedlinePlus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:51, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hyperparathyroidism | |
|---|---|
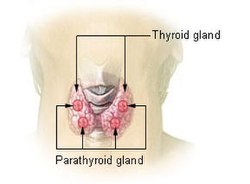
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, depression, bone pain, kidney stones, osteoporosis |
| Complications | Osteoporosis, kidney stones, cardiovascular disease |
| Onset | Typically middle age |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Overactivity of one or more of the parathyroid glands |
| Risks | Radiation therapy, genetic disorders |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests showing elevated calcium and parathyroid hormone levels |
| Differential diagnosis | Hypercalcemia, malignancy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, medication |
| Medication | Bisphosphonates, calcimimetics |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | 1-7 per 1,000 people |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition characterized by an overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands. This excess PTH can lead to high levels of calcium in the blood, which can cause a variety of health problems.

Types[edit]
- There are two main types of hyperparathyroidism: primary and secondary.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by an enlargement or adenoma in one or more of the parathyroid glands. This leads to an overproduction of PTH and subsequent high calcium levels in the blood.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism is a response to low calcium levels in the blood. This can be due to various reasons such as vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, or dietary insufficiency. The low calcium levels stimulate the parathyroid glands to produce more PTH.
Symptoms[edit]
- Hyperparathyroidism can often be asymptomatic, especially in its early stages. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Depression or forgetfulness
- Bone and joint pain
- Frequent urination
- Kidney stones
- Nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite
Diagnosis[edit]
Hyperparathyroidism is often diagnosed through blood tests that show high levels of PTH and calcium. Other tests, like bone density scans and kidney function tests, may also be used. In some cases, imaging tests can help identify an enlarged parathyroid gland.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In primary hyperparathyroidism, surgery to remove the affected parathyroid gland(s) may be necessary. For secondary hyperparathyroidism, treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause, such as increasing calcium or vitamin D intake or managing kidney disease.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
- Khan, Aliya (2017). "Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Diagnosis, Differential Diagnosis, and Evaluation". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
- Komaba, Hirotaka; Fukagawa, Masafumi (2012). "Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathogenesis and Treatment". Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis.
- Bilezikian, John P.; Khan, Aliya A.; Potts, John T. (2009). "Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: Summary statement from the Fourth International Workshop". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
External Links[edit]
Hyperparathyroidism - MedlinePlus Primary Hyperparathyroidism - Mayo Clinic Hyperparathyroidism - American Association of Endocrine Surgeons


