Tonic tensor tympani syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Tonic tensor tympani syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Depiction_of_a_patient_suffering_from_ear_pain_(Otalgia).png|250px]] | |||
| caption = Depiction of a patient suffering from ear pain (Otalgia) | |||
| field = [[Otolaryngology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Ear pain]], [[tinnitus]], [[hyperacusis]], [[ear fullness]] | |||
| onset = Any age | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Stress]], [[anxiety]], [[muscle tension]] | |||
| risks = [[Noise exposure]], [[stress]], [[anxiety disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical diagnosis]], [[audiometry]] | |||
| differential = [[Temporomandibular joint disorder]], [[Eustachian tube dysfunction]], [[Meniere's disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Cognitive behavioral therapy]], [[sound therapy]], [[muscle relaxants]] | |||
| medication = [[Benzodiazepines]], [[antidepressants]] | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| prognosis = Variable, often chronic | |||
}} | |||
'''Therapeutic privilege''' is a concept in [[medical ethics]] that allows a [[physician]] to withhold information from a [[patient]] if they believe that disclosing the information could lead to harm or distress for the patient. This is a controversial practice, as it can be seen as infringing on the patient's [[autonomy]] and right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare. | '''Therapeutic privilege''' is a concept in [[medical ethics]] that allows a [[physician]] to withhold information from a [[patient]] if they believe that disclosing the information could lead to harm or distress for the patient. This is a controversial practice, as it can be seen as infringing on the patient's [[autonomy]] and right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
Therapeutic privilege is often invoked in situations where a physician believes that the patient may become overly anxious or distressed if they are fully informed about their medical condition or the risks associated with a proposed treatment. The physician may choose to withhold certain information, or to present it in a way that minimizes the potential for distress. | Therapeutic privilege is often invoked in situations where a physician believes that the patient may become overly anxious or distressed if they are fully informed about their medical condition or the risks associated with a proposed treatment. The physician may choose to withhold certain information, or to present it in a way that minimizes the potential for distress. | ||
However, this practice is controversial. Critics argue that it infringes on the patient's autonomy and their right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare. They argue that patients have a right to know all relevant information about their health, even if it is distressing. | However, this practice is controversial. Critics argue that it infringes on the patient's autonomy and their right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare. They argue that patients have a right to know all relevant information about their health, even if it is distressing. | ||
== Ethical considerations == | == Ethical considerations == | ||
The concept of therapeutic privilege raises several ethical questions. One of the key issues is the balance between the patient's right to autonomy and the physician's duty to do no harm. While withholding information may prevent distress, it can also prevent the patient from making fully informed decisions about their healthcare. | The concept of therapeutic privilege raises several ethical questions. One of the key issues is the balance between the patient's right to autonomy and the physician's duty to do no harm. While withholding information may prevent distress, it can also prevent the patient from making fully informed decisions about their healthcare. | ||
Another ethical issue is the potential for abuse of therapeutic privilege. There is a risk that physicians may use this privilege to withhold information not for the benefit of the patient, but to protect themselves from potential legal action or to make their own job easier. | Another ethical issue is the potential for abuse of therapeutic privilege. There is a risk that physicians may use this privilege to withhold information not for the benefit of the patient, but to protect themselves from potential legal action or to make their own job easier. | ||
== Legal status == | == Legal status == | ||
The legal status of therapeutic privilege varies from country to country. In some jurisdictions, it is recognized as a valid exception to the requirement for informed consent. In others, it is not recognized at all, or is only recognized in very limited circumstances. | The legal status of therapeutic privilege varies from country to country. In some jurisdictions, it is recognized as a valid exception to the requirement for informed consent. In others, it is not recognized at all, or is only recognized in very limited circumstances. | ||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
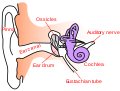
File:Ear-anatomy-text-small-en.svg|Diagram of ear anatomy | |||
File:Tympanometry.svg|Tympanometry test illustration | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Informed consent]] | * [[Informed consent]] | ||
* [[Medical ethics]] | * [[Medical ethics]] | ||
* [[Patient autonomy]] | * [[Patient autonomy]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Medical ethics]] | [[Category:Medical ethics]] | ||
[[Category:Health law]] | [[Category:Health law]] | ||
[[Category:Patient rights]] | [[Category:Patient rights]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:57, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tonic tensor tympani syndrome | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Ear pain, tinnitus, hyperacusis, ear fullness |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Any age |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Stress, anxiety, muscle tension |
| Risks | Noise exposure, stress, anxiety disorders |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, audiometry |
| Differential diagnosis | Temporomandibular joint disorder, Eustachian tube dysfunction, Meniere's disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Cognitive behavioral therapy, sound therapy, muscle relaxants |
| Medication | Benzodiazepines, antidepressants |
| Prognosis | Variable, often chronic |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Therapeutic privilege is a concept in medical ethics that allows a physician to withhold information from a patient if they believe that disclosing the information could lead to harm or distress for the patient. This is a controversial practice, as it can be seen as infringing on the patient's autonomy and right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare.
Introduction[edit]
Therapeutic privilege is often invoked in situations where a physician believes that the patient may become overly anxious or distressed if they are fully informed about their medical condition or the risks associated with a proposed treatment. The physician may choose to withhold certain information, or to present it in a way that minimizes the potential for distress. However, this practice is controversial. Critics argue that it infringes on the patient's autonomy and their right to make informed decisions about their own healthcare. They argue that patients have a right to know all relevant information about their health, even if it is distressing.
Ethical considerations[edit]
The concept of therapeutic privilege raises several ethical questions. One of the key issues is the balance between the patient's right to autonomy and the physician's duty to do no harm. While withholding information may prevent distress, it can also prevent the patient from making fully informed decisions about their healthcare. Another ethical issue is the potential for abuse of therapeutic privilege. There is a risk that physicians may use this privilege to withhold information not for the benefit of the patient, but to protect themselves from potential legal action or to make their own job easier.
Legal status[edit]
The legal status of therapeutic privilege varies from country to country. In some jurisdictions, it is recognized as a valid exception to the requirement for informed consent. In others, it is not recognized at all, or is only recognized in very limited circumstances.
Gallery[edit]
-
Diagram of ear anatomy
-
Tympanometry test illustration
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />