Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency | |||
| image =[[File:Autorecessive.svg|200px]] | |||
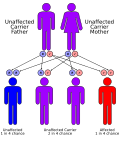
| caption = Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is inherited in an [[autosomal recessive]] pattern. | |||
| synonyms = ADSL deficiency, adenylosuccinase deficiency | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Developmental delay]], [[autism spectrum disorder]], [[epilepsy]], [[muscle weakness]] | |||
| onset = [[Infancy]] | |||
| duration = Lifelong | |||
| causes = Mutations in the [[ADSL gene]] | |||
| risks = Family history of the condition | |||
| diagnosis = [[Genetic testing]], [[metabolic screening]] | |||
| differential = [[Other inborn errors of purine metabolism]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[symptomatic treatment]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, often severe | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency | |||
{{Short description|A rare metabolic disorder affecting purine metabolism}} | {{Short description|A rare metabolic disorder affecting purine metabolism}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 4 April 2025
| Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | ADSL deficiency, adenylosuccinase deficiency |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Developmental delay, autism spectrum disorder, epilepsy, muscle weakness |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Infancy |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mutations in the ADSL gene |
| Risks | Family history of the condition |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, metabolic screening |
| Differential diagnosis | Other inborn errors of purine metabolism |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, symptomatic treatment |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, often severe |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency
A rare metabolic disorder affecting purine metabolism
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder that affects the purine metabolism pathway. It is characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme adenylosuccinate lyase (ASL), which plays a crucial role in the conversion of adenylosuccinate to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and fumarate. This deficiency leads to the accumulation of succinylpurines in the body, which can cause a variety of symptoms, primarily affecting the nervous system.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Adenylosuccinate lyase is an enzyme involved in two key reactions in the purine nucleotide cycle:
- The conversion of adenylosuccinate to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and fumarate.
- The conversion of succinylaminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (SAICAR) to aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICAR) and fumarate.
In individuals with adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency, mutations in the ASL gene lead to reduced or absent enzyme activity. This results in the accumulation of succinylpurines, which are toxic to the central nervous system.
Clinical features[edit]
The clinical presentation of adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency can vary widely among affected individuals. Common symptoms include:
The severity of symptoms can range from mild to severe, and some individuals may also experience intellectual disability.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is typically based on clinical evaluation, biochemical testing, and genetic analysis. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Measurement of succinylpurines in urine or cerebrospinal fluid using mass spectrometry.
- Genetic testing to identify mutations in the ASL gene.
Treatment[edit]
Currently, there is no cure for adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. Treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic, focusing on managing seizures, developmental delays, and other associated symptoms. Interventions may include:
- Antiepileptic drugs for seizure control.
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy to improve motor skills.
- Speech therapy to address communication difficulties.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency varies depending on the severity of the condition. Early diagnosis and intervention can help improve outcomes, but many individuals may continue to experience significant challenges throughout their lives.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
-
Lysine structure
-
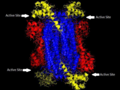
ASL active sites
-
S-adenosylmethionine
Adenylosuccinate_lyase_deficiency[edit]
-
Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
-
Lysine phosphorylation
-
Adenylosuccinate lyase active sites
-
S-adenosylmethionine space-filling model