Geology: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Study of the Earth and its processes}} | |||
{{other uses}} | |||
[[File:Book-hawaii-vtorov-142.jpg|thumb|right|A geological study in Hawaii]] | |||
'''Geology''' is the scientific study of the Earth, including its composition, structure, physical properties, and history. It is a major branch of the [[Earth sciences]] and encompasses the study of the solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Geology provides insights into the Earth's past, including the evolution of life and past climates, and helps predict future geological events and changes. | |||
== Branches of Geology == | ==Branches of Geology== | ||
Geology is a broad field that includes several sub-disciplines: | |||
* '''[[Petrology]]''': The study of rocks and the conditions under which they form. | |||
* '''[[Mineralogy]]''': The study of minerals, their structure, properties, and classification. | |||
* '''[[Paleontology]]''': The study of fossils and ancient life forms. | |||
* '''[[Sedimentology]]''': The study of sedimentary rocks and the processes of sedimentation. | |||
* '''[[Structural geology]]''': The study of rock formations and the forces that shape them. | |||
* '''[[Volcanology]]''': The study of volcanoes and volcanic phenomena. | |||
* '''[[Seismology]]''': The study of earthquakes and the propagation of seismic waves. | |||
==Geological Processes== | |||
Geological processes are dynamic and shape the Earth's surface over time. These include: | |||
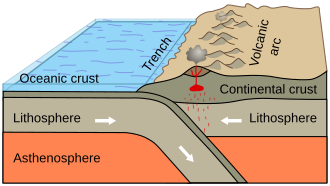
* '''[[Plate tectonics]]''': The movement of the Earth's lithospheric plates that leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. | |||
[[File:Plates_tect2_en.svg|thumb|left|Diagram of plate tectonics]] | |||
* '''[[Erosion]] and [[weathering]]''': The processes that break down rocks and transport sediments. | |||
* '''[[Sedimentation]]''': The deposition of sediments in layers, forming sedimentary rocks. | |||
* '''[[Metamorphism]]''': The alteration of rocks by heat, pressure, and chemical processes. | |||
* '''[[Volcanism]]''': The eruption of magma onto the Earth's surface, forming volcanic rocks. | |||
* [[Earth | ==The Rock Cycle== | ||
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology that describes the transformation of rocks through various geological processes. It involves the formation, breakdown, and reformation of rocks. | |||
[[File:Cycle_of_rocks_2.png|thumb|right|The rock cycle]] | |||
* '''Igneous rocks''' form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. | |||
* '''Sedimentary rocks''' form from the accumulation and lithification of sediments. | |||
* '''Metamorphic rocks''' form from the alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure. | |||
==Geological Time== | |||
Geological time is a system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time. It is used by geologists to describe the timing and relationships of events in Earth's history. The geological time scale is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages. | |||
==Applications of Geology== | |||
Geology has numerous practical applications, including: | |||
* '''[[Natural resource]] exploration''': Locating and extracting minerals, oil, and gas. | |||
* '''[[Environmental geology]]''': Assessing and mitigating environmental impacts of human activities. | |||
* '''[[Engineering geology]]''': Providing geological information for construction and infrastructure projects. | |||
* '''[[Hazard assessment]]''': Predicting and mitigating natural disasters such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
* [[Earth science]] | |||
* [[Geophysics]] | * [[Geophysics]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Geochemistry]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Geomorphology]] | ||
[[File:Badlands_at_Sunset.jpg|thumb|left|Badlands at sunset, showcasing geological formations]] | |||
[[File:Cheshire_Cat_(5121607167).jpg|thumb|right|Geological formations resembling a Cheshire Cat]] | |||
[[File:Or_Venezuela.jpg|thumb|left|Geological landscape in Venezuela]] | |||
[[File:Quartz,_Tibet.jpg|thumb|right|Quartz crystal from Tibet]] | |||
[[File:Active_Margin.svg|thumb|left|Diagram of an active margin]] | |||
[[Category:Geology]] | [[Category:Geology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 23 March 2025
Study of the Earth and its processes
Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its composition, structure, physical properties, and history. It is a major branch of the Earth sciences and encompasses the study of the solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Geology provides insights into the Earth's past, including the evolution of life and past climates, and helps predict future geological events and changes.
Branches of Geology[edit]
Geology is a broad field that includes several sub-disciplines:
- Petrology: The study of rocks and the conditions under which they form.
- Mineralogy: The study of minerals, their structure, properties, and classification.
- Paleontology: The study of fossils and ancient life forms.
- Sedimentology: The study of sedimentary rocks and the processes of sedimentation.
- Structural geology: The study of rock formations and the forces that shape them.
- Volcanology: The study of volcanoes and volcanic phenomena.
- Seismology: The study of earthquakes and the propagation of seismic waves.
Geological Processes[edit]
Geological processes are dynamic and shape the Earth's surface over time. These include:
- Plate tectonics: The movement of the Earth's lithospheric plates that leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity.

- Erosion and weathering: The processes that break down rocks and transport sediments.
- Sedimentation: The deposition of sediments in layers, forming sedimentary rocks.
- Metamorphism: The alteration of rocks by heat, pressure, and chemical processes.
- Volcanism: The eruption of magma onto the Earth's surface, forming volcanic rocks.
The Rock Cycle[edit]
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology that describes the transformation of rocks through various geological processes. It involves the formation, breakdown, and reformation of rocks.

- Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
- Sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation and lithification of sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks form from the alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
Geological Time[edit]
Geological time is a system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time. It is used by geologists to describe the timing and relationships of events in Earth's history. The geological time scale is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
Applications of Geology[edit]
Geology has numerous practical applications, including:
- Natural resource exploration: Locating and extracting minerals, oil, and gas.
- Environmental geology: Assessing and mitigating environmental impacts of human activities.
- Engineering geology: Providing geological information for construction and infrastructure projects.
- Hazard assessment: Predicting and mitigating natural disasters such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions.
Related Pages[edit]