Geophysics
Geophysics' is the scientific discipline that applies the principles of physics to the study of the Earth. It encompasses a broad range of sub-disciplines that explore the Earth's physical properties, including its gravitational and magnetic fields, internal structure, oceans, atmosphere, and climate. Geophysicists employ a variety of techniques to investigate the Earth, from surface observations to deep drilling and remote sensing methods. The ultimate goal of geophysics is to understand the processes that drive the Earth's dynamics and its interactions with the surrounding space environment.
Overview[edit]
Geophysics is inherently interdisciplinary, bridging the gap between physical geography, geology, meteorology, oceanography, and astronomy. It can be divided into two main areas: solid Earth geophysics and atmospheric geophysics. Solid Earth geophysics focuses on the Earth's core, mantle, and crust, exploring phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and plate tectonics. Atmospheric geophysics, on the other hand, deals with the study of the Earth's atmosphere, weather patterns, and climate change.
Sub-disciplines[edit]
Several key sub-disciplines within geophysics include:
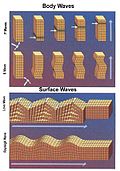
- Seismology: The study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth.
- Magnetotellurics: The investigation of the Earth's magnetic and electric fields to reveal the planet's subsurface electrical conductivity.
- Geodesy: The science of measuring and understanding the Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space, and gravity field.
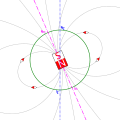
- Paleomagnetism: The study of the Earth's magnetic field in the past, which is preserved in rocks and sediments.
- Hydrogeology: The examination of groundwater and its properties, including its distribution and movement through the Earth's crust.
Techniques and Tools[edit]
Geophysicists employ a variety of tools and techniques to study the Earth, including:
- Seismic waves: Used in seismology to probe the Earth's interior structure.
- Satellite observations: Utilized in geodesy and atmospheric studies for precise measurements of the Earth's surface and atmosphere.
- Magnetic and gravity surveys: Conducted to map the Earth's magnetic and gravity fields, revealing clues about its internal structure.
- Electrical and electromagnetic methods: Applied in magnetotellurics and hydrogeology to investigate the subsurface conductivity and water content.
Applications[edit]
The applications of geophysics are vast and varied, including:
- Exploration for oil, gas, minerals, and groundwater.
- Earthquake hazard assessment and mitigation.
- Volcanic monitoring and prediction.
- Climate modeling and weather forecasting.
- Environmental studies and pollution tracking.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit]
Geophysics faces several challenges, such as the need for more accurate and comprehensive models of the Earth's interior, better understanding of the complex interactions between the Earth's surface and atmosphere, and the development of more sophisticated tools and techniques for data collection and analysis. Future directions in geophysics may include increased use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to analyze complex datasets, more integrated approaches to studying the Earth system as a whole, and enhanced collaboration across different scientific disciplines.

This article is a geophysics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Age of Ocean Plates
-
Geodynamo Between Reversals
-
Earth Gravity
-
Convection Snapshot
-
P and S Waves
-
Geomagnetism
-
Thorium Decay Chain
-
Earthquake Wave Paths
-
Structure of the Magnetosphere
-
East Han Seismograph
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian