Actinism: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Photography]] | [[Category:Photography]] | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
Latest revision as of 03:35, 17 March 2025
- Actinism
Actinism refers to the property of solar radiation that leads to the production of photochemical effects. This term is derived from the Greek word "aktis," meaning ray or beam, and is primarily associated with the chemical changes induced by light, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Overview[edit]
Actinism is a crucial concept in various scientific fields, including photography, dermatology, and botany. It describes the ability of light to cause chemical reactions, which is a fundamental principle in processes such as photosynthesis and the degradation of materials exposed to sunlight.
Historical Context[edit]
The concept of actinism was first recognized in the early 19th century when scientists began to understand the effects of light beyond mere illumination. The discovery of actinism was pivotal in the development of photographic techniques, as it explained how light could alter chemical compounds on photographic plates.
Scientific Basis[edit]
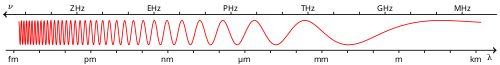
Actinism is primarily associated with the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, although visible light can also exhibit actinic properties. The energy carried by UV light is sufficient to break chemical bonds, leading to photochemical reactions. This is why UV light is often used in sterilization and disinfection processes.
Photochemical Reactions[edit]
Photochemical reactions are chemical reactions initiated by the absorption of light. These reactions are essential in various natural and industrial processes. For example, in photosynthesis, plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, a process driven by the actinic properties of light.
Applications[edit]
- **Photography**: Actinism is the principle behind the exposure of photographic film. Light-sensitive chemicals on the film react to light, capturing images.
- **Dermatology**: Understanding actinism is crucial in dermatology, particularly in the study of skin damage caused by UV radiation, such as sunburn and skin cancer.
- **Material Science**: Actinism is considered in the study of material degradation, as prolonged exposure to sunlight can lead to the breakdown of materials like plastics and paints.
Also see[edit]
| Electromagnetic spectrum | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
higher frequencies, higher energy, shorter wavelengths longer wavelengths, lower frequencies, lower energy →
|