Triazolobenzodiazepine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
__NOINDEX__ | __NOINDEX__ | ||
== Triazolobenzodiazepine == | == Triazolobenzodiazepine == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Alprazolam_structure.svg|Alprazolam structure | File:Alprazolam_structure.svg|Alprazolam structure | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:08, 17 March 2025
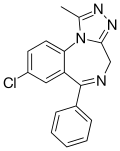
Triazolobenzodiazepine is a class of benzodiazepine drugs that includes several well-known medications used primarily for the treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizure disorders. These drugs are characterized by the presence of a triazole ring fused to the benzodiazepine structure.
Chemical Structure
Triazolobenzodiazepines are a subclass of benzodiazepines. They are distinguished by the addition of a triazole ring to the basic benzodiazepine structure. This modification results in drugs with different pharmacological properties compared to other benzodiazepines.
Pharmacology
Triazolobenzodiazepines work by enhancing the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces the activity of neurons. By enhancing the effect of GABA, triazolobenzodiazepines help to calm the brain and reduce symptoms of anxiety and insomnia.
Examples
Examples of triazolobenzodiazepines include alprazolam (Xanax), triazolam (Halcion), and estazolam (ProSom). These drugs are commonly prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia.
Side Effects
Like all benzodiazepines, triazolobenzodiazepines can cause side effects. These may include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and dependence. Long-term use can lead to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
See Also
References
<references />
Triazolobenzodiazepine
-
Alprazolam structure