Baird-Parker agar: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
[[Category:Microbiological media]] | [[Category:Microbiological media]] | ||
== Baird-Parker agar gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
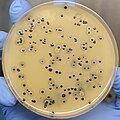
File:S. aureus colonies in Baird-Parker agar.jpg|S. aureus colonies in Baird-Parker agar | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:32, 3 March 2025
Baird-Parker Agar
Baird-Parker Agar is a selective culture medium primarily used for the isolation and enumeration of coagulase-positive staphylococci, particularly *Staphylococcus aureus*, from food, clinical, and environmental samples. This medium is named after the microbiologists Baird and Parker, who developed it in 1962.
Composition[edit]
Baird-Parker Agar contains several key components that make it selective and differential:
- Tryptone and Beef Extract: Provide essential nutrients and growth factors for bacterial growth.
- Yeast Extract: Supplies vitamins and additional growth factors.
- Sodium Pyruvate: Enhances the recovery of stressed cells and improves the growth of staphylococci.
- Glycine: Inhibits the growth of competing bacteria.
- Lithium Chloride: Acts as a selective agent against non-staphylococcal organisms.
- Egg Yolk Emulsion: Provides lecithin and lipids, which are hydrolyzed by lecithinase-positive staphylococci, resulting in a clear zone around colonies.
- Potassium Tellurite: Inhibits most gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive bacteria, while allowing the growth of *Staphylococcus aureus*, which reduces tellurite to tellurium, forming black colonies.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Baird-Parker Agar is both selective and differential. The selectivity is achieved through the use of lithium chloride and potassium tellurite, which suppress the growth of most non-staphylococcal bacteria. The differential aspect is due to the egg yolk emulsion, which allows the detection of lecithinase activity. Colonies of *Staphylococcus aureus* appear as black or gray due to tellurite reduction, often surrounded by a clear zone of egg yolk precipitation.
Procedure[edit]
1. Sample Preparation: Prepare the sample by homogenizing it in a suitable diluent. 2. Inoculation: Spread the sample onto the surface of the Baird-Parker Agar plate. 3. Incubation: Incubate the plates at 35-37°C for 24-48 hours. 4. Examination: Examine the plates for characteristic black colonies with clear zones.
Interpretation[edit]
- Positive Result: Black colonies with clear zones indicate the presence of coagulase-positive staphylococci, such as *Staphylococcus aureus*.
- Negative Result: Absence of black colonies or presence of colonies without clear zones suggests the absence of coagulase-positive staphylococci.
Applications[edit]
Baird-Parker Agar is widely used in:
- Food Microbiology: To test for contamination by *Staphylococcus aureus* in food products.
- Clinical Diagnostics: To isolate *Staphylococcus aureus* from clinical specimens.
- Environmental Monitoring: To assess the presence of staphylococci in environmental samples.
Limitations[edit]
While Baird-Parker Agar is effective for isolating *Staphylococcus aureus*, it may not differentiate between all coagulase-positive staphylococci. Some strains may not produce the characteristic black colonies, and additional confirmatory tests, such as the coagulase test, may be necessary.
Also see[edit]
| Microbiology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This microbiology related article is a stub.
|
Baird-Parker agar gallery[edit]
-
S. aureus colonies in Baird-Parker agar