Furazolidone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
[[Category:Nitrofuran antibiotics]] | [[Category:Nitrofuran antibiotics]] | ||
[[Category:Withdrawn drugs]] | [[Category:Withdrawn drugs]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
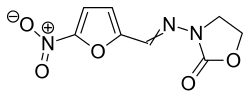
File:Furazolidone.svg|Furazolidone | |||
File:Furazolidone 3D spacefill.png|Furazolidone 3D Spacefill | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:38, 20 February 2025
An article about the use of Furazolidone in medicine
| Furazolidone | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Furazolidone is an antimicrobial agent that has been used in the treatment of bacterial and protozoal infections. It belongs to the class of nitrofuran antibiotics and has been used in both human and veterinary medicine.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Furazolidone works by interfering with the DNA of bacteria and protozoa, inhibiting their ability to reproduce and repair themselves. This action is primarily bacteriostatic, meaning it stops bacteria from multiplying, but it can also be bactericidal at higher concentrations.
Medical Uses[edit]
Furazolidone has been used to treat a variety of infections, including:
- Giardiasis
- Cholera
- Bacterial diarrhea
- Helicobacter pylori infections
It is particularly effective against infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria and some protozoa.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of furazolidone include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
Rare but serious side effects can include:
Contraindications[edit]
Furazolidone should not be used in individuals with known hypersensitivity to nitrofuran derivatives. It is also contraindicated in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency due to the risk of hemolytic anemia.
Drug Interactions[edit]
Furazolidone can interact with other medications, including:
These interactions can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular effects.
Regulatory Status[edit]
Furazolidone has been withdrawn from the market in many countries due to concerns about its safety profile and the availability of safer alternatives. However, it may still be used in some regions under specific circumstances.
Also see[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Furazolidone
-
Furazolidone 3D Spacefill