Neurodegenerative disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
[[Category:Aging and the brain]] | [[Category:Aging and the brain]] | ||
[[Category:Dementia]] | [[Category:Dementia]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Alzheimer's disease brain comparison.jpg|Neurodegenerative disease | |||
File:Alzheimers brain.jpg|Neurodegenerative disease | |||
File:Hazard ratio lag for replicated viral infection–neurodegenerative disease pairs.jpg|Neurodegenerative disease | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 00:40, 20 February 2025
Neurodegenerative disease refers to a group of progressive disorders characterized by the gradual loss of function and structure of neurons, leading to cognitive decline, motor dysfunction, and other neurological impairments. These diseases are typically chronic and incurable, with increasing prevalence due to aging populations.
Pathophysiology
Neurodegenerative diseases involve progressive neuronal death caused by multiple pathological mechanisms, including:
- Protein misfolding and aggregation – Accumulation of misfolded proteins such as:
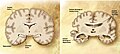
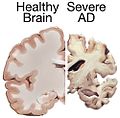
- Beta-amyloid and tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease.
- Huntingtin protein in Huntington’s disease.
- Mitochondrial dysfunction – Impairment in cellular respiration leading to oxidative stress.
- Excitotoxicity – Overactivation of glutamate receptors causing neuronal damage.
- Neuroinflammation – Chronic activation of microglia and astrocytes contributing to cell damage.
- Genetic mutations – Inherited mutations in genes such as APP, PSEN1, PSEN2 (Alzheimer’s) or HTT (Huntington’s disease).
Types of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are classified based on the primary affected neuronal system:
Alzheimer’s and Related Dementias
- Alzheimer’s disease – Characterized by memory loss, cognitive decline, and beta-amyloid plaques.
- Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) – Affects behavior, personality, and language skills.
- Lewy body dementia – Involves alpha-synuclein deposits and symptoms of both dementia and Parkinson’s disease.
- Vascular dementia – Caused by impaired blood flow to the brain, leading to cognitive decline.
Movement Disorders
- Parkinson’s disease – Affects dopaminergic neurons, leading to tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA) – A progressive disorder with autonomic dysfunction and movement impairment.
- Huntington’s disease – A genetic disorder causing involuntary movements and cognitive decline.
- Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) – Characterized by difficulty in eye movement, balance, and speech problems.
Motor Neuron Diseases
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig’s disease) – Affects the motor neurons, leading to progressive paralysis.
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) – A genetic disorder affecting lower motor neurons.
- Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) – A rare form of motor neuron disease affecting the upper motor neurons.
Prion Diseases
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) – A rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease caused by abnormal prion proteins.
- Kuru – A prion disease historically found in the Fore people of Papua New Guinea.
- Fatal familial insomnia (FFI) – A rare, genetic prion disease causing insomnia and neurodegeneration.
Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to neurodegenerative disease development:
- Aging – The biggest risk factor, as neuronal function declines with age.
- Genetics – Family history increases risk for diseases like Huntington’s disease and ALS.
- Environmental exposure – Toxins, heavy metals, pesticides, and air pollution may contribute.
- Lifestyle factors – Poor diet, lack of exercise, and chronic stress may increase risk.
- Traumatic brain injury – Linked to chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) in athletes.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the specific disease but often include:
- Cognitive impairment – Memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with decision-making.
- Motor dysfunction – Tremors, muscle weakness, rigidity, or loss of coordination.
- Behavioral changes – Mood swings, personality changes, and emotional instability.
- Speech and swallowing difficulties – Common in ALS, Parkinson’s disease, and FTD.
- Autonomic dysfunction – Blood pressure fluctuations and bladder control issues in diseases like MSA.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases involves:
- Neurological examination – Assessing cognitive and motor functions.
- Neuroimaging:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – Identifies brain atrophy and structural changes.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) – Detects protein aggregates and metabolic activity.
- Genetic testing – Identifies mutations in inherited neurodegenerative diseases.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis – Used in Alzheimer’s disease to detect beta-amyloid and tau protein levels.
- Electromyography (EMG) – Assesses motor neuron function in ALS.
Treatment and Management
There are no cures for neurodegenerative diseases, but treatments can slow progression and alleviate symptoms.
Pharmacological Treatments
- Cholinesterase inhibitors (Donepezil, Rivastigmine) – Used for Alzheimer’s disease.
- Dopamine agonists (Levodopa) – Improve Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
- Glutamate antagonists (Riluzole) – Prolong survival in ALS.
- Antipsychotics – Used cautiously in Lewy body dementia and frontotemporal dementia.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
- Physical therapy – Improves mobility and balance in Parkinson’s disease and ALS.
- Speech therapy – Helps manage communication difficulties.
- Dietary and lifestyle modifications – Antioxidant-rich diets, exercise, and social engagement may reduce risk.
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS) – A surgical treatment for Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor.
Future Research and Experimental Therapies
Emerging treatments include:
- Gene therapy – Targeting specific genetic mutations in SMA and Huntington’s disease.
- Stem cell therapy – Investigating neuronal regeneration.
- Immunotherapy – Targeting abnormal protein aggregates with monoclonal antibodies.
- CRISPR gene editing – Potential future treatments for inherited neurodegenerative disorders.
Prognosis
The prognosis varies depending on the specific disease:
- Alzheimer’s disease – Progressive cognitive decline over 5–20 years.
- Parkinson’s disease – Slowly progressive but manageable with treatment.
- ALS – Life expectancy of 2–5 years after diagnosis.
- Prion diseases – Rapidly fatal within months to a few years.
Prevention
While no definitive prevention exists, strategies to reduce risk include:
- Regular exercise – Supports brain plasticity and vascular health.
- Cognitive engagement – Activities like reading, puzzles, and social interactions may slow cognitive decline.
- Healthy diet – Diets like the Mediterranean diet may have protective effects.
- Avoidance of toxins – Limiting exposure to pesticides and heavy metals.
- Managing chronic conditions – Controlling diabetes, hypertension, and obesity reduces risk.
Related Pages
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Neurodegeneration
- Huntington’s disease
- Dementia
-
Neurodegenerative disease
-
Neurodegenerative disease
-
Neurodegenerative disease