Algestone acetophenide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
File:Algestone_acetophenide_availability.png|Availability of Algestone acetophenide | File:Algestone_acetophenide_availability.png|Availability of Algestone acetophenide | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Algestone Acetophenide == | |||
'''Algestone acetophenide''', also known as dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide, is a synthetic progestogen, a type of [[progestin]] used in [[hormonal contraception]]. It is a derivative of [[progesterone]], a naturally occurring hormone involved in the [[menstrual cycle]], [[pregnancy]], and embryogenesis of humans and other species. | |||
== Chemical Structure and Properties == | |||
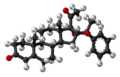
Algestone acetophenide is a [[steroid]] with a chemical structure that is closely related to that of progesterone. It is characterized by the presence of an acetophenide group, which is a phenylacetate ester. This modification enhances its progestogenic activity and alters its pharmacokinetic properties, making it suitable for use in long-acting contraceptive formulations. | |||
== Mechanism of Action == | |||
As a progestogen, algestone acetophenide works primarily by mimicking the effects of natural progesterone. It binds to [[progesterone receptors]] in the body, leading to changes in the [[endometrium]] that prevent [[ovulation]] and make the uterine lining less suitable for [[implantation]] of a fertilized egg. Additionally, it thickens the [[cervical mucus]], making it more difficult for [[sperm]] to enter the [[uterus]]. | |||
== Clinical Use == | |||
Algestone acetophenide is used in combination with [[estradiol enantate]] in some [[combined injectable contraceptives]]. These contraceptives are administered via [[intramuscular injection]] and provide effective birth control for a period of one month. The combination of a progestogen with an [[estrogen]] helps to regulate the [[menstrual cycle]] and reduce the risk of [[breakthrough bleeding]]. | |||
== Pharmacokinetics == | |||
After intramuscular injection, algestone acetophenide is slowly released into the bloodstream, providing a sustained level of the hormone. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine. The long half-life of the drug allows for monthly dosing, which is convenient for users. | |||
== Side Effects == | |||
Common side effects of algestone acetophenide, as with other progestogens, may include [[weight gain]], [[headache]], [[breast tenderness]], and changes in [[menstrual bleeding patterns]]. Some users may experience [[amenorrhea]] or [[irregular bleeding]]. Serious side effects are rare but can include [[thromboembolic events]] and [[liver dysfunction]]. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Progestogen]] | |||
* [[Hormonal contraception]] | |||
* [[Progesterone]] | |||
* [[Estradiol enantate]] | |||
* [[Menstrual cycle]] | |||
{{Contraception}} | |||
{{Hormones}} | |||
[[Category:Progestogens]] | |||
[[Category:Contraception]] | |||
[[Category:Steroids]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:35, 19 February 2025
-
Chemical structure of Algestone acetophenide
-
Ball-and-stick model of Algestone acetophenide
-
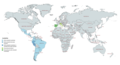
Availability of Algestone acetophenide
Algestone Acetophenide[edit]
Algestone acetophenide, also known as dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide, is a synthetic progestogen, a type of progestin used in hormonal contraception. It is a derivative of progesterone, a naturally occurring hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Algestone acetophenide is a steroid with a chemical structure that is closely related to that of progesterone. It is characterized by the presence of an acetophenide group, which is a phenylacetate ester. This modification enhances its progestogenic activity and alters its pharmacokinetic properties, making it suitable for use in long-acting contraceptive formulations.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
As a progestogen, algestone acetophenide works primarily by mimicking the effects of natural progesterone. It binds to progesterone receptors in the body, leading to changes in the endometrium that prevent ovulation and make the uterine lining less suitable for implantation of a fertilized egg. Additionally, it thickens the cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to enter the uterus.
Clinical Use[edit]
Algestone acetophenide is used in combination with estradiol enantate in some combined injectable contraceptives. These contraceptives are administered via intramuscular injection and provide effective birth control for a period of one month. The combination of a progestogen with an estrogen helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the risk of breakthrough bleeding.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
After intramuscular injection, algestone acetophenide is slowly released into the bloodstream, providing a sustained level of the hormone. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine. The long half-life of the drug allows for monthly dosing, which is convenient for users.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of algestone acetophenide, as with other progestogens, may include weight gain, headache, breast tenderness, and changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. Some users may experience amenorrhea or irregular bleeding. Serious side effects are rare but can include thromboembolic events and liver dysfunction.
Related Pages[edit]
| Hormones | ||
|---|---|---|
|