Estradiol enantate
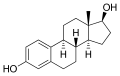
Estradiol enantate (EE), also spelled estradiol enanthate, is a form of estrogen used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and in hormonal contraception. It is a long-acting ester of estradiol, the primary female sex hormone, and is administered via intramuscular injection.
Medical Uses[edit]
Estradiol enantate is primarily used in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal atrophy, and osteoporosis. It is also used in contraception in combination with a progestogen. The medication provides a long-term release of estradiol, making it a convenient option for individuals seeking sustained hormone levels.
Pharmacology[edit]
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
As an estrogen, estradiol enantate binds to and activates the estrogen receptor (ER), leading to the regulation of gene transcription and expression in estrogen-responsive tissues. This action is responsible for its effects on the reproductive system, bone density, and the maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Following intramuscular injection, estradiol enantate is slowly absorbed into the bloodstream, providing a prolonged duration of action. This allows for less frequent dosing schedules compared to other forms of estrogen therapy. The ester is eventually hydrolyzed, releasing estradiol, which is then metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine and feces.
Adverse Effects[edit]
The use of estradiol enantate can lead to side effects similar to those of other estrogen therapies, including nausea, breast tenderness, headache, and an increased risk of thromboembolic events. Long-term use may also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and endometrial cancer, although the risk varies depending on whether a progestogen is used in combination with estradiol enantate.
Contraindications[edit]
Estradiol enantate is contraindicated in individuals with known hypersensitivity to the drug, those with a history of estrogen-dependent tumors, active or recent thromboembolic disease, and unexplained vaginal bleeding. It should also be used with caution in patients with liver dysfunction, gallbladder disease, and in those with a history of depression.
Interactions[edit]
Estradiol enantate may interact with various medications, including cytochrome P450 substrates, anticoagulants, and thyroid hormone replacement therapy. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for a complete list of potential interactions.
Pharmaceutical Information[edit]
Estradiol enantate is available in various formulations and dosages for intramuscular injection. The choice of dosage and frequency of administration should be individualized based on the patient's needs and response to therapy.
Society and Culture[edit]
Estradiol enantate has been used in medical practice for several decades and is included in some formulations of combined injectable contraceptives. Its role in hormone therapy for transgender individuals is also recognized, although specific guidelines may vary.
See Also[edit]
-
Estradiol enanthate
-
Estradiol enanthate molecule ball
-
Estradiol
-
Estradiol levels after an intramuscular injection of different doses of estradiol enanthate in premenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels after a single intramuscular injection of 10 mg estradiol enantate in postmenopausal women
-
Estradiol and prolactin levels after the last injection during therapy with estradiol enantate and dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide in women
-
Estradiol levels with estradiol enanthate and dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide after single or repeated injections in premenopausal women
-
Idealized curves of estradiol levels after injection of different estradiol esters in women
-
Estradiol enanthate availability
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian