Combined injectable birth control: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Women's health]] | [[Category:Women's health]] | ||
{{contraception-stub}} | {{contraception-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
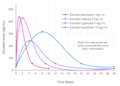
File:Idealized_curves_of_estradiol_levels_after_injection_of_different_estradiol_esters_in_women.png|Idealized curves of estradiol levels after injection of different estradiol esters in women | |||
File:Hormone_levels_in_men_with_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_5_mg_estradiol_valerate_and_50_mg_norethisterone_enanthate_in_oil.png|Hormone levels in men with a single intramuscular injection of 5 mg estradiol valerate and 50 mg norethisterone enanthate in oil | |||
File:Combined_injectable_contraceptive_availability.png|Combined injectable contraceptive availability | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:26, 18 February 2025
Combined injectable birth control (CIBC) is a type of hormonal contraception that is administered through injection. It contains two types of hormones: an estrogen and a progestin, which work together to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus to block sperm, and thin the lining of the uterus to prevent a fertilized egg from implanting.
Composition[edit]
The two hormones used in CIBC are typically estradiol or estradiol valerate (forms of estrogen) and a progestin such as medroxyprogesterone acetate or norethisterone enanthate. The specific combination of hormones can vary depending on the brand and formulation of the injectable birth control.
Administration[edit]
CIBC is typically administered once a month by a healthcare provider. The injection is usually given in the muscle of the upper arm or buttock. It is important to receive the injections on schedule to maintain effective contraception.
Efficacy[edit]
When used correctly, CIBC is a highly effective method of contraception. The failure rate is less than 1% per year, which is comparable to other forms of hormonal contraception such as the combined oral contraceptive pill.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of CIBC can include menstrual irregularities, weight gain, breast tenderness, and mood changes. Less common but more serious side effects can include blood clots, stroke, and heart attack, particularly in women who smoke or have other risk factors.
Advantages and disadvantages[edit]
Advantages of CIBC include its high efficacy, convenience (only needing to be administered once a month), and the fact that it does not interfere with sexual activity. Disadvantages can include the potential for side effects, the need for regular injections, and the fact that it does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
See also[edit]
- Contraception
- Hormonal contraception
- Combined oral contraceptive pill
- Progestogen-only injectable contraceptive
This contraception related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Idealized curves of estradiol levels after injection of different estradiol esters in women
-
Hormone levels in men with a single intramuscular injection of 5 mg estradiol valerate and 50 mg norethisterone enanthate in oil
-
Combined injectable contraceptive availability