Nitrobenzene: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
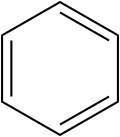
File:Benzol.svg|Benzene structure | |||
File:Nitronium_ion_vert.svg|Nitronium ion | |||
File:Nitrobenzol.svg|Nitrobenzene structure | |||
File:Synthesis_of_4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane.svg|Synthesis of 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 03:46, 18 February 2025
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents.
Production[edit]
Nitrobenzene is produced by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production steps are similar to those used in the production of nitric acid.
Uses[edit]
The main use of nitrobenzene is in the production of aniline. Nitrobenzene is also used to manufacture lubricating oils such as those found in automobiles and machinery. It is also used in the production of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and polymers.
Safety[edit]
Nitrobenzene is toxic and can be absorbed through the skin. Prolonged exposure can lead to a condition called methemoglobinemia, where the blood's ability to carry oxygen is reduced.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />