Cell death: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Cell death]] | [[Category:Cell death]] | ||
{{cell-biology-stub}} | {{cell-biology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Signal_transduction_pathways.svg|Signal transduction pathways | |||
File:Apoptotic_cell_disassembly.png|Apoptotic cell disassembly | |||
File:Autophagy.jpg|Autophagy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:47, 18 February 2025
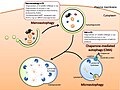
Cell death refers to the biological process in which a cell ceases to carry out its functions and ultimately dies. This process is a crucial part of the life cycle of all multicellular organisms and plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis and organism health. There are several types of cell death, including apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy, each with its own unique characteristics and functions.
Types of Cell Death[edit]
Apoptosis[edit]
Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. It is a highly regulated and controlled process that plays a crucial role in development, tissue homeostasis, and immunity. During apoptosis, the cell undergoes changes such as cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, and chromatin condensation.
Necrosis[edit]
Necrosis is a form of cell death that results from acute cellular injury. Unlike apoptosis, necrosis is not a programmed process and often leads to inflammation due to the release of intracellular components.
Autophagy[edit]
Autophagy is a process in which a cell degrades its own components through the lysosomal machinery. It is a survival mechanism in response to nutrient deprivation but can also lead to cell death under certain conditions.
Role in Disease[edit]
Cell death plays a significant role in various diseases. For instance, excessive cell death can lead to degenerative diseases, while insufficient cell death can result in uncontrolled cell proliferation, as seen in cancer.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a cell biology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Signal transduction pathways
-
Apoptotic cell disassembly
-
Autophagy