Sulfisomidine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Sulfonamides]] | [[Category:Sulfonamides]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Sulfisomidine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
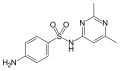
File:Sulfisomidine.svg|Chemical structure of Sulfisomidine | |||
File:Sulfisomidine_ball-and-stick.png|Ball-and-stick model of Sulfisomidine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:03, 18 February 2025
Sulfisomidine (also known as sulfafurazole) is a sulfonamide antibacterial medication. It is used in the treatment of various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and skin infections.
History[edit]
Sulfisomidine was first synthesized in the 1930s as part of a series of compounds known as sulfonamides, which were the first effective systemic antibacterial agents. The discovery of sulfonamides marked a significant turning point in the history of medicine, as it led to the development of the modern field of chemotherapy.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Sulfisomidine, like other sulfonamides, works by inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, which is involved in the synthesis of folic acid. Bacteria need folic acid to survive and reproduce, so by inhibiting its production, sulfisomidine effectively kills the bacteria.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of sulfisomidine include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In rare cases, it can cause serious side effects such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hemolytic anemia.
Drug Interactions[edit]
Sulfisomidine can interact with several other medications, including methotrexate, warfarin, and certain diabetes medications. It can also interact with certain foods, particularly those high in folic acid, as this can reduce the effectiveness of the drug.
See Also[edit]
Sulfisomidine[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Sulfisomidine
-
Ball-and-stick model of Sulfisomidine