Desoxypipradrol: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Desoxypipradrol == | |||
<gallery> | |||
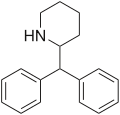
File:Desoxypipradrol.svg|Chemical structure of Desoxypipradrol | |||
File:Desoxypipradrol_3D.gif|3D model of Desoxypipradrol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:10, 17 February 2025
Desoxypipradrol (also known as 2-DPMP, 2-diphenylmethylpiperidine, or 2-benzhydrylpiperidine) is a stimulant drug of the piperidine class. It was developed in the 1950s by the pharmaceutical company CIBA (now Novartis) as a potential treatment for narcolepsy and ADHD, but was never commercially marketed.
Chemistry[edit]
Desoxypipradrol is a synthetic compound of the piperidine class. The chemical structure consists of a piperidine ring, which is a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom and five carbon atoms, substituted at the 2 position with a diphenylmethyl group.
Pharmacology[edit]
Desoxypipradrol acts as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI), meaning it increases the levels of the norepinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitters in the brain by inhibiting their reuptake into neurons. This results in increased neuronal activity, which can lead to increased alertness and wakefulness.
Effects[edit]
The effects of desoxypipradrol can vary greatly depending on the dose and individual's physiology. At lower doses, it can produce effects such as increased alertness, wakefulness, and focus. At higher doses, it can cause effects such as restlessness, insomnia, and increased heart rate.
Legal Status[edit]
Desoxypipradrol is a controlled substance in many countries due to its potential for abuse and addiction. In the United States, it is classified as a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
Desoxypipradrol[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Desoxypipradrol
-
3D model of Desoxypipradrol