Lirequinil: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
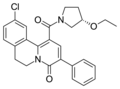
File:Lirequinil_structure.png|Structure of Lirequinil | |||
File:Ro41-3290_structure.png|Structure of Ro41-3290 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:55, 17 February 2025
Lirequinil is a sedative and anxiolytic drug that was developed by a team at NeuroSearch. It is a nonbenzodiazepine, but its structure is quite different from most other nonbenzodiazepine drugs, and it is thought to have a different mechanism of action.
Pharmacology[edit]
Lirequinil is a GABA_A receptor partial agonist, which means it produces only a partial effect at the GABA_A receptor compared to a full agonist. This makes it less potent than full agonist drugs and may reduce the risk of side effects such as sedation and amnesia.
Development and Clinical Trials[edit]
Lirequinil was developed as a potential treatment for insomnia and anxiety, but it was discontinued after Phase II clinical trials due to poor results. The drug was found to be less effective than other treatments for insomnia, and it had a higher rate of side effects.
Side Effects[edit]
The most common side effects of Lirequinil include dizziness, nausea, and headache. Some patients also reported feeling fatigued or sleepy during the day. These side effects were more common in patients taking higher doses of the drug.