Acetohexamide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Sulfonylureas]] | [[Category:Sulfonylureas]] | ||
[[Category:Antidiabetic drugs]] | [[Category:Antidiabetic drugs]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
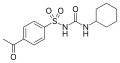
File:Acetohexamide.svg|Acetohexamide structure diagram | |||
File:Acetohexamide_ball-and-stick.png|Acetohexamide ball-and-stick model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:52, 17 February 2025
A sulfonylurea antidiabetic drug
| Acetohexamide | |
|---|---|
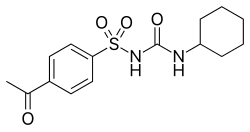
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Acetohexamide is an oral hypoglycemic agent belonging to the sulfonylurea class of drugs. It is used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus to lower blood glucose levels.
Mechanism of Action
Acetohexamide works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin. It binds to the sulfonylurea receptor on the beta cells of the pancreas, leading to the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. This results in the depolarization of the cell membrane and the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, which increases intracellular calcium and triggers insulin release.
Pharmacokinetics
Acetohexamide is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes hepatic metabolism. It is metabolized to an active metabolite, hydroxyhexamide, which also contributes to its hypoglycemic effect. The drug and its metabolites are excreted primarily in the urine.
Clinical Use
Acetohexamide is indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients who cannot achieve adequate glycemic control with diet and exercise alone. It is typically used as a second-line therapy after metformin or in combination with other antidiabetic agents.
Side Effects
Common side effects of acetohexamide include hypoglycemia, nausea, and dizziness. Rare but serious side effects can include hematological disorders, allergic reactions, and liver dysfunction.
Contraindications
Acetohexamide is contraindicated in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis, and those with known hypersensitivity to sulfonylureas. Caution is advised in patients with renal impairment or hepatic impairment.
Related pages
Gallery
-
Structural formula of Acetohexamide
-
Ball-and-stick model of Acetohexamide
-
Acetohexamide structure diagram
-
Acetohexamide ball-and-stick model