Activated protein C resistance test: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Hematology]] | [[Category:Hematology]] | ||
[[Category:Medical tests]] | [[Category:Medical tests]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
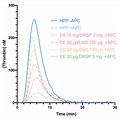
File:Thrombin_generation_curves_with_and_without_activated_protein_C_and_with_various_oral_contraceptives_with_activated_protein_C.png|Thrombin generation curves with and without activated protein C and with various oral contraceptives with activated protein C | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:46, 17 February 2025
Activated Protein C Resistance Test[edit]
The Activated Protein C Resistance Test is a laboratory assay used to evaluate the resistance of blood plasma to activated protein C (APC). This test is primarily used to diagnose Factor V Leiden mutation, which is the most common hereditary cause of thrombophilia.
Background[edit]
Activated protein C is a natural anticoagulant that inactivates Factor Va and Factor VIIIa, thereby reducing thrombin generation and preventing excessive blood clotting. Resistance to activated protein C is often due to a genetic mutation in the Factor V gene, known as Factor V Leiden, which makes Factor Va resistant to inactivation by APC.
Test Procedure[edit]
The activated protein C resistance test is performed by measuring the clotting time of plasma in the presence and absence of activated protein C. The test is typically conducted using a partial thromboplastin time (PTT) assay. The ratio of the clotting time with APC to the clotting time without APC is calculated. A lower ratio indicates resistance to activated protein C.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Resistance to activated protein C is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Identifying individuals with APC resistance, particularly those with the Factor V Leiden mutation, is important for assessing thrombotic risk and guiding management strategies.
Interpretation[edit]
A normal result indicates that the plasma is sensitive to activated protein C, while an abnormal result suggests resistance. Further genetic testing may be performed to confirm the presence of the Factor V Leiden mutation.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Thrombin generation curves with and without activated protein C.
-
Thrombin generation curves with and without activated protein C and with various oral contraceptives with activated protein C